Testosterone: Difference between revisions
imported>Gareth Leng No edit summary |
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
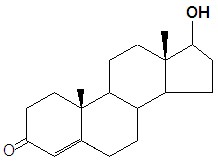
{{Image|Testosterone stickfig DEVolk.jpg|right|350px|Structure of testosterone.}} | |||
'''Testosterone''' is a [[steroid]] hormone that has been widely abused to enhance athletic performance because it is an [[anabolic steroid]] that stimulates growth. Testosterone is an [[androgen]] that controls virulization (masculinity). It is derived from another androgen, [[androstenedione]], and is a chemical precurson to the [[estrogen]] steroid [[estradiol]]. Testosterone is mainly secreted from the [[testes]], but some is also produced in the [[adrenal glands]], so it is present in females as well as in males, but at much lower concentrations. Testosterone acts at specific nuclear receptors expressed in many tissues of the body, including the [[pituitary gland]], and at some sites in the brain where it exerts effects on behaviour and regulates secretion of some hormones. In the brain, testosterone can also be metabolised (by the enzyme [[aromatase]])to produce [[oestrogen]]. Testosterone has a negative feedback effect on the secretion of [[luteinising hormone]] and [[follicle stimulating hormone]], which in men promote testis growth and sperm production. Accordingly, excessive levels of testosterone, while they result in muscle enhancement and increased aggression, can also result in hypogonadism (reduction in testis size) and infertility. | '''Testosterone''' is a [[steroid]] hormone that has been widely abused to enhance athletic performance because it is an [[anabolic steroid]] that stimulates growth. Testosterone is an [[androgen]] that controls virulization (masculinity). It is derived from another androgen, [[androstenedione]], and is a chemical precurson to the [[estrogen]] steroid [[estradiol]]. Testosterone is mainly secreted from the [[testes]], but some is also produced in the [[adrenal glands]], so it is present in females as well as in males, but at much lower concentrations. Testosterone acts at specific nuclear receptors expressed in many tissues of the body, including the [[pituitary gland]], and at some sites in the brain where it exerts effects on behaviour and regulates secretion of some hormones. In the brain, testosterone can also be metabolised (by the enzyme [[aromatase]])to produce [[oestrogen]]. Testosterone has a negative feedback effect on the secretion of [[luteinising hormone]] and [[follicle stimulating hormone]], which in men promote testis growth and sperm production. Accordingly, excessive levels of testosterone, while they result in muscle enhancement and increased aggression, can also result in hypogonadism (reduction in testis size) and infertility. | ||
Revision as of 07:57, 8 June 2009
Testosterone is a steroid hormone that has been widely abused to enhance athletic performance because it is an anabolic steroid that stimulates growth. Testosterone is an androgen that controls virulization (masculinity). It is derived from another androgen, androstenedione, and is a chemical precurson to the estrogen steroid estradiol. Testosterone is mainly secreted from the testes, but some is also produced in the adrenal glands, so it is present in females as well as in males, but at much lower concentrations. Testosterone acts at specific nuclear receptors expressed in many tissues of the body, including the pituitary gland, and at some sites in the brain where it exerts effects on behaviour and regulates secretion of some hormones. In the brain, testosterone can also be metabolised (by the enzyme aromatase)to produce oestrogen. Testosterone has a negative feedback effect on the secretion of luteinising hormone and follicle stimulating hormone, which in men promote testis growth and sperm production. Accordingly, excessive levels of testosterone, while they result in muscle enhancement and increased aggression, can also result in hypogonadism (reduction in testis size) and infertility.
Its chemical IUPAC name is 8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17S)-17-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-1,2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15, 16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one and its molecular formula is C19H28O2.
brand names
- Andriol
- Andro
- Andro 100
- Andro L.A. 200
- Androderm
- Androgel
- Android 10
- Android 25
- Android 5
- Androlin
- Andronaq
- Andronate 100
- Andronate 200
- Andropatch
- Andropository 200
- Andrusol
- Andryl 200
- Beta Testosterone
- CDB 111C
- Cristerona T
- Cristerone T
- Delatest
- Delatestryl
- Depo-Testosterone
- Depo-Testosterone Cypionate
- Depotest
- Everone 200
- Geno-Cristaux Gremy
- Homosteron
- Homosterone
- Libigel
- Malerone
- Malestrone
- Malogen in Oil
- Malogen, Aquaspension Injection
- Mertestate
- Metandren
- Methyltestosterone
- Neo-Hombreol F
- Neo-Testis
- Neotestis
- Oreton
- Oreton F
- Oreton Methyl
- Oreton-F
- Orquisteron
- Perandren
- Percutacrine Androgenique
- Primotest
- Primoteston
- Relibra
- Scheinpharm Testone-Cyp
- Striant
- Sustanon
- Sustanone
- Sustason 250
- Synandrol F
- T-Cypionate
- Teslen
- Testamone 100
- Testandrone
- Testaqua
- Testiculosterone
- Testim
- Testobase
- Testoderm
- Testoderm Tts
- Testogel
- Testoject-50
- Testolin
- Testopel Pellets
- Testopropon
- Testosteroid
- Testoviron
- Testoviron Schering
- Testoviron T
- Testred
- Testred Cypionate 200
- Testrin-P.A
- Testro Aq
- Testrone
- Testryl
- Virilon
- Virilon IM
- Virormone
- Virosterone