Leflunomide: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk (brand name) |
imported>David E. Volk (DailyMed template) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== drug interactions == | == drug interactions == | ||
Leflunomide increases the anticoagulation effects of [[anisindione]], [[acenocoumarol]] and [[dicumarol]] and [[warfarin]]. [[Rifampin]] increases the effect of leflunomide. | Leflunomide increases the anticoagulation effects of [[anisindione]], [[acenocoumarol]] and [[dicumarol]] and [[warfarin]]. [[Rifampin]] increases the effect of leflunomide. | ||
== External Links == | |||
* {{DailyMed}} | |||
Revision as of 14:18, 24 January 2008
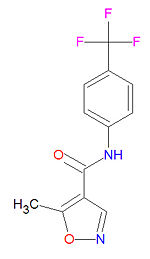
Leflunomide, with IUPAC name 5-methyl-N-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamide and chemical formula C12H9F3N2O2, also called leflunomidum and lefunomide, is a pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor belonging to the DMARD (disease-modifying antirheumatic drug) class of drugs used to treat rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Activated T cells, which are increased in patients with RA, are dependent on de novo pyrimidine synthesis and will thus be more affected by leflunomide's inhibition of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase than other cell types that use the salvage pathway of pyrimidine synthesis. It is sold under the brand name Arava.
drug interactions
Leflunomide increases the anticoagulation effects of anisindione, acenocoumarol and dicumarol and warfarin. Rifampin increases the effect of leflunomide.
External Links
- Leflunomide - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).