Energy storage: Difference between revisions
imported>David MacQuigg m (correcting cost example) |
(add WNA chart of energy storage for various fuels) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{seealso|Nuclear_power_reconsidered}} | {{seealso|Nuclear_power_reconsidered}} | ||
{{TOC|right}} | {{TOC|right}} | ||
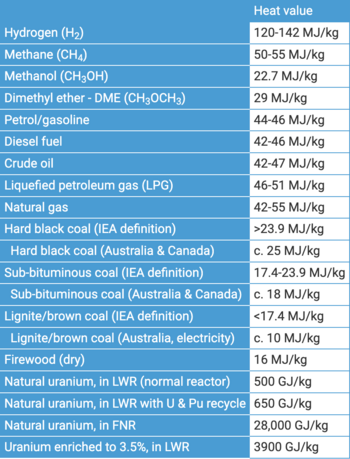
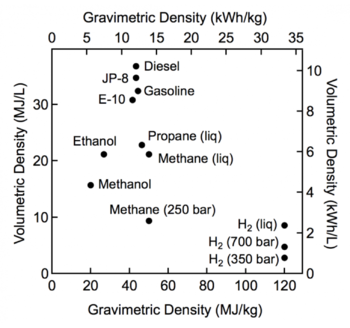
{{Image|Fuel Energy Density.png|right|350px|Fig.1 Comparison of specific energy (energy per mass or gravimetric density) and energy density (energy per volume or volumetric density) for several fuels.<ref>https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/hydrogen-storage</ref>}} | |||
{{Image|Fuel Energy Density WNA.png|right|350px|Add image caption here.}} | |||
This article is a brief comparison of the technologies relevant to the large-scale energy storage<ref>https://world-nuclear.org/information-library/current-and-future-generation/electricity-and-energy-storage.aspx</ref> needed for wind and solar and other intermittent energy sources. | This article is a brief comparison of the technologies relevant to the large-scale energy storage<ref>https://world-nuclear.org/information-library/current-and-future-generation/electricity-and-energy-storage.aspx</ref> needed for wind and solar and other intermittent energy sources. | ||
The most important point of comparison is cost per kilowatt hour (kWh) of storage, including the cost of ancillary equipment like power inverters or heat storage tanks. Other costs, like battery replacement can be included by assuming a reasonable time over which these capital costs are depreciated.<ref>For example, a $100M system providing 1000 megawatt hours (MWh) total storage would have a capital cost of $100/kWh. If 80% of that system had to be replaced every 100 months, using straight-line depreciation, the monthly cost would be $800,000. Add that to the financing cost, say 0.5% per month, and other operating costs, maybe another 0.5% per month, and the total monthly cost is $1.8M.</ref> | The most important point of comparison is cost per kilowatt hour (kWh) of storage, including the cost of ancillary equipment like power inverters or heat storage tanks. Other costs, like battery replacement can be included by assuming a reasonable time over which these capital costs are depreciated.<ref>For example, a $100M system providing 1000 megawatt hours (MWh) total storage would have a capital cost of $100/kWh. If 80% of that system had to be replaced every 100 months, using straight-line depreciation, the monthly cost would be $800,000. Add that to the financing cost, say 0.5% per month, and other operating costs, maybe another 0.5% per month, and the total monthly cost is $1.8M.</ref> | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
==Hydrogen== | ==Hydrogen== | ||
Hydrogen energy storage may become an important competitor to pumped hydro and thermal, especially if high-temperature nuclear reactors become available. | Hydrogen energy storage may become an important competitor to pumped hydro and thermal, especially if high-temperature nuclear reactors become available. | ||
The abundant high-temperature heat from these reactors will offset the inefficiency of generating the hydrogen from water. The volumetric energy density of hydrogen is too low for transportation uses (see Fig.1) but is not a problem for utilities. | The abundant high-temperature heat from these reactors will offset the inefficiency of generating the hydrogen from water. The volumetric energy density of hydrogen is too low for transportation uses (see Fig.1) but is not a problem for utilities. | ||
Revision as of 23:40, 20 April 2022
- See also: Nuclear_power_reconsidered
This article is a brief comparison of the technologies relevant to the large-scale energy storage[2] needed for wind and solar and other intermittent energy sources. The most important point of comparison is cost per kilowatt hour (kWh) of storage, including the cost of ancillary equipment like power inverters or heat storage tanks. Other costs, like battery replacement can be included by assuming a reasonable time over which these capital costs are depreciated.[3]
Other factors to consider in buying energy storage are the peak power needed and the round-trip-efficiency. Pumped hydro and batteries return about 80% of the energy put in.[4] Thermal storage, where there is no conversion to other forms of energy, can be near 100% efficient.
In a power grid with a mix of intermittent and dispatchable sources, and insufficient storage, the capital cost of the dispatchable sources is determined by the peak demand on the grid. Adding intermittent sources reduces only the fuel costs of the dispatchable sources, not their capital costs.
Pumped hydro
This is the energy storage most widely used by utilities, where available. Near a river with a big reservoir, cost per kWh can be very low, limited only by the cost of operating the motor/pump/turbine/generator. Where water is limited, the capital cost of building the reservoirs, upper and lower, should be divided by the total storage capacity and this result added to the operating cost per kWh.[5]
Thermal
There are many technologies for storing heat,[6] but for concentrated solar power (CSP) systems, the choice has been molten salt.[7] Thermal storage is also being considered at nuclear plants to allow rapid load following in grids that have a large component of wind and solar.[8] Research is continuing on on sensible, latent, and thermochemical energy storage with a goal of $15 per kWh.[9]
Batteries
Batteries are still too expensive for most utility-scale systems. Even with an optimistic projection of future Li-ion battery technology ($100 per kWh) a small city with 1 GW average consumption might need 100 hours of storage, requiring a $10 billion capital investment, ten times the cost of the plant.[10] Some newer battery technologies promise lower cost per kWh, but at the scale needed to power the world, there may be resource limitations.[11]
Hydrogen
Hydrogen energy storage may become an important competitor to pumped hydro and thermal, especially if high-temperature nuclear reactors become available. The abundant high-temperature heat from these reactors will offset the inefficiency of generating the hydrogen from water. The volumetric energy density of hydrogen is too low for transportation uses (see Fig.1) but is not a problem for utilities.
Other
Although not storing energy to be used for generating electricity, high-temperature reactors can perform the equivalent of energy storage by using excess available energy to power processes that don't care if the energy is intermittent, like the production of steel, cement, and fertilizer. This "process heat" is a big part of our world energy consumption, and can be timed to take advantage of periods when the intermittent sources are at full power.
Further reading
- Electricity and Energy Storage World Nuclear Association.
Notes and References
- ↑ https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/hydrogen-storage
- ↑ https://world-nuclear.org/information-library/current-and-future-generation/electricity-and-energy-storage.aspx
- ↑ For example, a $100M system providing 1000 megawatt hours (MWh) total storage would have a capital cost of $100/kWh. If 80% of that system had to be replaced every 100 months, using straight-line depreciation, the monthly cost would be $800,000. Add that to the financing cost, say 0.5% per month, and other operating costs, maybe another 0.5% per month, and the total monthly cost is $1.8M.
- ↑ https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=46756
- ↑ To store 100 megawatts for 10 hours you will need a hill 500 feet high with 250 acre reservoirs at each end that you can draw up or down 10 feet.
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thermal_energy_storage
- ↑ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Concentrated_solar_power
- ↑ https://natriumpower.com/
- ↑ Thermal Storage R&D for CSP Systems | Department of Energy
- ↑ Liquid metal batteries might cut this cost in half. https://ambri.com/technology
- ↑ The Liquid Metal Battery uses low-cost calcium as the anode, but antimony for the cathodes may be in short supply if this technology is scaled up.