Flare stack: Difference between revisions
imported>Milton Beychok m (Replaced image with more relevant one.) |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
A '''flare stack''' or '''gas flare''' is a tall vertical vent pipe used in [[Petroleum refining processes|petroleum refineries]], [[petrochemical plant]]s, [[chemical plant]]s and [[Natural gas processing|natural gas processing plants]] for burning off flammable [[gas]] released by pressure [[relief valve]]s during unplanned over-pressuring of plant equipment.<ref>{{cite book|author=John J McKetta, Editor|title=Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design|publisher=Marcel Dekker|year=1985|pages=144|id=ISBN 0-8247-2491-7}}</ref><ref name=Beychok>{{cite book|author=Milton R. Beychok|title=[[Fundamentals of Stack Gas Dispersion]]|edition=Fourth edition|publisher=self-published |year=2005|id=ISBN 0-9644588-0-2}} See Chapter 11, ''Flare Stack Plume Rise''.</ref><ref>[http://aiche.confex.com/aiche/s06/techprogram/P40539.HTM A Proposed Comprehensive Model for Elevated Flare Flames and Plumes], David Shore, Flaregas Corporation, [[AIChE]] 40th Loss Prevention Symposium, April 2006.</ref> | A '''flare stack''' or '''gas flare''' is a tall vertical vent pipe used in [[Petroleum refining processes|petroleum refineries]], [[petrochemical plant]]s, [[chemical plant]]s and [[Natural gas processing|natural gas processing plants]] for burning off flammable [[gas]] released by pressure [[relief valve]]s during unplanned over-pressuring of plant equipment.<ref>{{cite book|author=John J McKetta, Editor|title=Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design|publisher=Marcel Dekker|year=1985|pages=144|id=ISBN 0-8247-2491-7}}</ref><ref name=Beychok>{{cite book|author=Milton R. Beychok|title=[[Fundamentals of Stack Gas Dispersion]]|edition=Fourth edition|publisher=self-published |year=2005|id=ISBN 0-9644588-0-2}} See Chapter 11, ''Flare Stack Plume Rise''.</ref><ref>[http://aiche.confex.com/aiche/s06/techprogram/P40539.HTM A Proposed Comprehensive Model for Elevated Flare Flames and Plumes], David Shore, Flaregas Corporation, [[AIChE]] 40th Loss Prevention Symposium, April 2006.</ref> | ||
When crude oil is extracted and produced from oil wells, natural gas associated with the oil is produced to | However, a great deal of flaring has nothing to do with protection against the dangers of over-pressuring industrial plant equipment. When [[Petroleum crude oil|crude oil]] is extracted and produced from oil wells, [[Natural gas|raw natural gas]] associated with the oil is produced to the surface as well. In areas of the world lacking pipelines and other gas transportation infrastructure, vast amounts of such associated gas are commonly flared as waste or unusable gas. | ||
the surface as well. In areas of the world lacking pipelines and other infrastructure, | |||
gas | The flaring of associated gas may occur at the top of a vertical flare stack (as in the adjacent photograph) or it may occur in a ground-level flare in an earthen pit. | ||
==The purpose of industrial plant flare stacks== | ==The purpose of industrial plant flare stacks== | ||
In industrial plants such as petroleum refineries, petrochemical or other chemical plants, and natural gas processing plants, the main purpose of a flare stack is that of safety by protecting [[pressure vessels]] or [[Piping (engineering)|pipes]] from over-pressuring due to unplanned upsets. | In industrial plants such as petroleum refineries, petrochemical or other chemical plants, and natural gas processing plants, the main purpose of a flare stack is that of safety by protecting [[pressure vessels]] or [[Piping (engineering)|pipes]] from over-pressuring due to unplanned operational upsets. | ||
Whenever any plant equipment items are over-pressured, [[pressure relief | Whenever any plant equipment items are over-pressured, [[pressure]] [[relief valve]]s automatically release gas and sometimes liquids as well. The released gases and/or liquids are routed to a flare stack and burned as they exit the flare stack. | ||
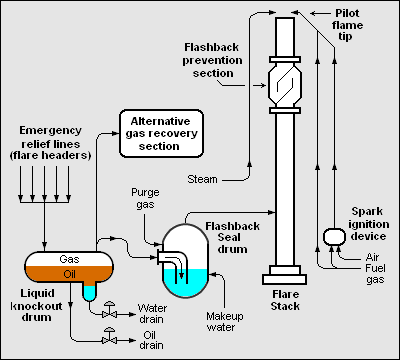
{{Image|FlareStack System.png|right|400px|Schematic flow diagram of overall flare stack system.}} | |||
==How industrial plant flare stacks work== | ==How industrial plant flare stacks work== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
The released gases and liquids are routed through large [[Piping (engineering)|piping]] systems called ''flare headers'' to a flare stack. The released gases are [[Combustion|burned]] as they exit the flare stacks. The size and brightness of the resulting flame depends upon the flammable material's flow rate in terms of [[Joule|joules]] per hour (or [[U.S. customary units|btu]] per hour).<ref name=Beychok/> | The released gases and liquids are routed through large [[Piping (engineering)|piping]] systems called ''flare headers'' to a flare stack. The released gases are [[Combustion|burned]] as they exit the flare stacks. The size and brightness of the resulting flame depends upon the flammable material's flow rate in terms of [[Joule|joules]] per hour (or [[U.S. customary units|btu]] per hour).<ref name=Beychok/> | ||
Most flares have a [[Vapor-liquid separator|vapor-liquid separator]] upstream of the flare to remove any large amounts of liquid that may accompany the relieved gases. | Most industrial plant flares have a [[Vapor-liquid separator|vapor-liquid separator]] (also known as a knockout drum) upstream of the flare to remove any large amounts of liquid that may accompany the relieved gases. | ||
[[Steam]] is very often injected into the flame to reduce the formation of black smoke. In order to keep the flare system functional, a small amount of gas is continuously burned, like a pilot light, so that the system is always ready for its primary purpose as an over-pressure safety system. | |||
The adjacent flow diagram depicts the typical components of an overall industrial flare stack system: | |||
*A knockout drum to remove any oil and/or water from the relieved gases. | |||
*A water seal drum to prevent any flashback of the flame from the the top of the flare stack. | |||
*As alternative gas recovery system for use during partial plant startups and/or shutdowns as well as other times when required. The recovered gas is routed into the fuel gas system of the overall industrial plant. | |||
*A steam injection system to provide an external momentum force used for efficient mixing of air with the relieved gas, which promotes smokeless burning. | |||
*A pilot flame (with its ignition system) that burns all the time so that it is available to ignite relieved gases whenever needed. | |||
*The flare stack, including a flashback prevention section at the upper part of the flare stack. | |||
==Environmental impacts of flaring associated gas from oil drilling sites == | ==Environmental impacts of flaring associated gas from oil drilling sites == | ||
{{Image|Nigerian gas flare.jpg|right|300px|Ground-flaring of associated gas from an oil well site in Nigeria.}} | |||
As of the end of 2011, 150 × 10<sup>9</sup> cubic meters (5.3 × 10<sup>12</sup> cubic feet) of associated gas are flared annually. That is equivalent to about 25% of the annual natural gas consumption in the [[United States of America]] or about 30% of the annual gas consumption in the [[European Union]].<ref name=GGFR>[http://siteresources.worldbank.org/INTGGFR/Resources/GGFR_NewBrochure%28Oct2011%29.pdf Global Gas Flaring Reduction Partnership (GGFR), World Bank]. October 2011 Brochure.</ref> | |||
That amount of flaring and burning of associated gas from oil drilling sites is a significant source of [[carbon dioxide]] (CO<sub>2</sub>) emissions. Some 400 × 10<sup>6</sup> tons of carbon dioxide are emitted annually in this way and it amounts to about 1.2% of the worldwide emissions of carbon dioxide. That may seem to be insignificant, but in perspective it is more than half of the Certified Emissions Reductions (a type of carbon credits) that have been issued under the rules and mechanisms of the Kyoto Protocol as of June 2011.<ref name=GGFR/><ref>[http://web.worldbank.org/WBSITE/EXTERNAL/NEWS/0,,contentMDK:21032487~menuPK:34480~pagePK:64257043~piPK:437376~theSitePK:4607,00.html Global Gas Flaring Reduction]. From the website of the World Bank.</ref> | |||
Satellite data on global gas flaring show that the current efforts to reduce gas flaring are paying off. From 2005 to 2010, the global estimate for gas flaring decreased by about 20%. The most significant reductions in terms of volume were made in Russia and Nigeria.<ref name=GGFR/><ref>[http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/dmsp/interest/flare_docs/NGDC_annual_report_20110209.pdf Estimation of Gas Flaring Volumes Using NASA MODIS Fire Detection Products]. NOAA's National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC) annual report, February 2011.</ref> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references/> | <references/>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:00, 17 August 2024
A flare stack or gas flare is a tall vertical vent pipe used in petroleum refineries, petrochemical plants, chemical plants and natural gas processing plants for burning off flammable gas released by pressure relief valves during unplanned over-pressuring of plant equipment.[1][2][3]
However, a great deal of flaring has nothing to do with protection against the dangers of over-pressuring industrial plant equipment. When crude oil is extracted and produced from oil wells, raw natural gas associated with the oil is produced to the surface as well. In areas of the world lacking pipelines and other gas transportation infrastructure, vast amounts of such associated gas are commonly flared as waste or unusable gas.
The flaring of associated gas may occur at the top of a vertical flare stack (as in the adjacent photograph) or it may occur in a ground-level flare in an earthen pit.
The purpose of industrial plant flare stacks
In industrial plants such as petroleum refineries, petrochemical or other chemical plants, and natural gas processing plants, the main purpose of a flare stack is that of safety by protecting pressure vessels or pipes from over-pressuring due to unplanned operational upsets.
Whenever any plant equipment items are over-pressured, pressure relief valves automatically release gas and sometimes liquids as well. The released gases and/or liquids are routed to a flare stack and burned as they exit the flare stack.
How industrial plant flare stacks work
Whenever plant equipment items are over-pressured, the pressure relief valves provided as essential safety devices on the equipment automatically release gases and sometimes liquids as well. Those pressure relief valves are required by industrial design codes and standards as well as by law.
The released gases and liquids are routed through large piping systems called flare headers to a flare stack. The released gases are burned as they exit the flare stacks. The size and brightness of the resulting flame depends upon the flammable material's flow rate in terms of joules per hour (or btu per hour).[2]
Most industrial plant flares have a vapor-liquid separator (also known as a knockout drum) upstream of the flare to remove any large amounts of liquid that may accompany the relieved gases.
Steam is very often injected into the flame to reduce the formation of black smoke. In order to keep the flare system functional, a small amount of gas is continuously burned, like a pilot light, so that the system is always ready for its primary purpose as an over-pressure safety system.
The adjacent flow diagram depicts the typical components of an overall industrial flare stack system:
- A knockout drum to remove any oil and/or water from the relieved gases.
- A water seal drum to prevent any flashback of the flame from the the top of the flare stack.
- As alternative gas recovery system for use during partial plant startups and/or shutdowns as well as other times when required. The recovered gas is routed into the fuel gas system of the overall industrial plant.
- A steam injection system to provide an external momentum force used for efficient mixing of air with the relieved gas, which promotes smokeless burning.
- A pilot flame (with its ignition system) that burns all the time so that it is available to ignite relieved gases whenever needed.
- The flare stack, including a flashback prevention section at the upper part of the flare stack.
Environmental impacts of flaring associated gas from oil drilling sites
As of the end of 2011, 150 × 109 cubic meters (5.3 × 1012 cubic feet) of associated gas are flared annually. That is equivalent to about 25% of the annual natural gas consumption in the United States of America or about 30% of the annual gas consumption in the European Union.[4]
That amount of flaring and burning of associated gas from oil drilling sites is a significant source of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions. Some 400 × 106 tons of carbon dioxide are emitted annually in this way and it amounts to about 1.2% of the worldwide emissions of carbon dioxide. That may seem to be insignificant, but in perspective it is more than half of the Certified Emissions Reductions (a type of carbon credits) that have been issued under the rules and mechanisms of the Kyoto Protocol as of June 2011.[4][5]
Satellite data on global gas flaring show that the current efforts to reduce gas flaring are paying off. From 2005 to 2010, the global estimate for gas flaring decreased by about 20%. The most significant reductions in terms of volume were made in Russia and Nigeria.[4][6]
References
- ↑ John J McKetta, Editor (1985). Encyclopedia of Chemical Processing and Design. Marcel Dekker, 144. ISBN 0-8247-2491-7.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Milton R. Beychok (2005). Fundamentals of Stack Gas Dispersion, Fourth edition. self-published. ISBN 0-9644588-0-2. See Chapter 11, Flare Stack Plume Rise.
- ↑ A Proposed Comprehensive Model for Elevated Flare Flames and Plumes, David Shore, Flaregas Corporation, AIChE 40th Loss Prevention Symposium, April 2006.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Global Gas Flaring Reduction Partnership (GGFR), World Bank. October 2011 Brochure.
- ↑ Global Gas Flaring Reduction. From the website of the World Bank.
- ↑ Estimation of Gas Flaring Volumes Using NASA MODIS Fire Detection Products. NOAA's National Geophysical Data Center (NGDC) annual report, February 2011.