Schrödinger equation: Difference between revisions
imported>Michael Evans No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (55 intermediate revisions by 12 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
The '''Schrödinger equation''' is one of the fundamental equations of [[quantum mechanics]] and describes the spatial and temporal behavior of quantum-mechanical systems. [[Austria]]n [[physicist]] [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1933/schrodinger.html Erwin Schrödinger] first proposed the equation in early 1926. Actually there are two different equations known as Schrödinger equation: The first is sometimes called the time-dependent, while the second is called the time independent equation, though in reality, it is simply an equation derived from the first using a mathematical technique known as [[separation of variables]]. The second one is an eigenvalue equation, written commonly as ''H''ψ = ''E'' ψ. The conditions that must be met to enable this separation of variables arise very frequently in chemistry and physics. It should also be noted that the fact that the time independent equation takes the form of a simple eigenvalue problem (thus being more amenable to mathematical analysis) that makes it so useful. | |||
Mathematically, the time-independent Schrödinger equation is an example of an [[eigenvalue problem]] whose eigenvectors ψ are called "wavefunctions" or "quantum states" and whose eigenvalues ''E'' correspond to [[energy level|energy levels]]. In many cases these energies can have only certain discrete values, which one expresses by stating that the energies are ''quantized''. | |||
Built into the eigenvectors are the probabilities of measuring all values of all physical [[observable|observables]], meaning that a solution of the Schrödinger equation provides a complete physical description of a system. Both Schrödinger equations contain an energy operator ''H'', called a [[Hamiltonian]]. In the case that the quantum system has a classical counterpart, the Hamiltonian operator is obtained by replacing the terms in the classical Hamiltonian function by [[linear operator]]s. | |||
We start by assuming that a beam of particles will have a wavefunction of the form | ==The Schrödinger wave equation== | ||
The wavefunction describes a wave of probability, the square of whose amplitude is equal to the probability of finding a particle at position ''x'' and time ''t''. But what is the form of Schrödinger's equation, which describes the time and position evolution of the wavefunction? The following is an introduction intended to provide some plausibility for the equation, but of course it is not possible to ''derive'' the Schrödinger equation because it is a fundamental ''postulate'' of quantum mechanics. | |||
We start by assuming that a beam of particles, like a beam of light, will have a wavefunction of the form | |||
:<math>\ \psi(x,t) = A \exp (i(kx-\omega t- \phi))</math> | :<math>\ \psi(x,t) = A \exp (i(kx-\omega t- \phi))</math> | ||
The square of this function (its probability amplitude) is a constant independent of position and time, which makes sense for a constant beam of particles: there is an equal probability of finding a particle at every point along the beam and any time. Using [[de Broglie hypothesis|de Broglie's relations]], | The absolute square |ψ|<sup>2</sup> of this function (its probability amplitude) is a constant independent of position and time, which makes sense for a constant beam of particles: there is an equal probability of finding a particle at every point along the beam and any time. Using [[de Broglie hypothesis|de Broglie's relations]], | ||
:<math>\ p = \hbar | :<math>\ p = \frac{\hbar \cdot 2 \pi}{\lambda} = \hbar k</math> | ||
:<math>\ E = \hbar \omega</math> | :<math>\ E = \hbar \omega</math>, | ||
where <math>\hbar\,</math> is [[Planck's constant]] divdided by 2π. | |||
Based on the functional form of <math>\psi</math>, we see that | Based on the functional form of <math>\psi</math>, we see that | ||
| Line 21: | Line 25: | ||
:<math>E \psi = \hbar \omega \psi = -\frac{\hbar}{i}\frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}=\hbar i \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}</math> | :<math>E \psi = \hbar \omega \psi = -\frac{\hbar}{i}\frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}=\hbar i \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}</math> | ||
Using the classical relationship between energy and momentum, | Using the classical relationship between kinetic energy and momentum and allowing for a potential, | ||
:<math>\ E \psi = [\frac{p^2}{2m}+V(x)] \psi</math> | :<math>\ E \psi = [\frac{p^2}{2m}+V(x)] \psi</math> | ||
Substituting for ''p'' and ''E'' yields the one-dimensional time-dependent Schrödinger equation, | Substituting for ''p'' and ''E'' yields the one-dimensional time-dependent Schrödinger wave equation, | ||
:<math>\hbar i \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2 \psi}{\partial x^2} + V(x) \psi</math> | :<math>\hbar i \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2 \psi}{\partial x^2} + V(x) \psi</math> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 36: | ||
:<math>E \psi=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2 \psi}{\partial x^2} + V(x) \psi</math> | :<math>E \psi=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{\partial^2 \psi}{\partial x^2} + V(x) \psi</math> | ||
[[Category: | |||
=== Generalising to several dimensions === | |||
In three dimensions, the second derivative becomes the [[Laplacian]]: | |||
:<math>\hbar i \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m} \nabla ^2 \psi + V(x,y,z) \psi</math> | |||
In spherical coordinates, the spherical definition of the Laplacian gives | |||
:<math>\hbar i \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t}=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2 \mu} \frac{1}{r^2 \sin \theta}\left[ \sin \theta \frac{\partial}{\partial r} \left( r^2 \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial r} \right)+\frac{\partial}{\partial \theta} \left( \sin \theta \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial \theta} \right)+\frac{1}{\sin \theta} \frac{\partial ^2 \psi}{\partial \phi ^2} \right] + V(r,\theta,\phi) \psi</math> | |||
Note that the heuristic reasoning in this section makes the form of the Schrödinger equation plausible, but should not be seen as a formal derivation departing from certain axioms. Indeed, it is generally assumed that the (time-dependent) Schrödinger equation itself is one of the central axioms of quantum mechanics.<ref name=axioms > | |||
For example, see {{cite book |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=0nags-BqlSQC&pg=PA95 |pages=pp. 95 ''ff'' |title=Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Information and Computation and Its Applications to Nano- and Bio-systems |author=Masanori Ohya, Igor Volovich |year=2011 |isbn=9400701705 |chapter= §5.11: Seven principles of quantum mechanics |publisher=Springer}} and {{cite web |title=Axiomatic/ Postulatory quantum mechanics |author=Mukul Agrawal |date=4 January, 2002 |url=http://www.stanford.edu/~mukul/tutorials/Quantum_Mechanics.pdf }} | |||
</ref> | |||
== The time-independent equation == | |||
The time-independent S.E. has the form | |||
:<math> - \frac{\hbar ^2}{2m} \nabla ^2 \psi + V(\mathbf{r}) \psi= E \psi</math> | |||
where | |||
:<math>-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m} \nabla ^2 + V(x,y,z) = \hat H</math> | |||
is the Hamiltonian operator. E is the mechanical energy of the particle wave. | |||
''H'' is an example of a quantum-mechanical [[operator]], the [[Hamiltonian]] (classical Hamiltonians also exist). It must be a [[self-adjoint]] operator because its eigenvalues ''E'' are the discrete, real energy levels of the system. Also, the various eigenfunctions <math>\psi_n</math> must be linearly independent and in fact form a basis for the state space of the system. In other words, the state of any system is reducible to a linear combination of solutions of the Schrödinger equation for that system. The Hamiltonian essentially contains all of the energy "sources" of the system, and its eigenstates describe the possible state of the system entirely. | |||
As an example, consider a particle in a one-dimensional box with infinite potential walls and a finite potential ''a'' inside the box. The Hamiltonian of this system is | |||
:<math>\hat H = -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m} \nabla ^2 + a</math> | |||
The first term of the Hamiltonian corresponds to the classical expression for kinetic energy, ''p''<sup>2</sup>/2''m'' (see above), and the second term is the potential energy as defined. No other sources of energy exist in the system as defined, and so the particle's state must be some linear combination of the eigenstates of ''H''. | |||
==A more general formulation== | |||
===Quantum state vectors=== | |||
The eigenfunctions of the Schrödinger equation form a basis for the state space of the system. This means that any quantum state can be written as a column vector, each entry of which corresponds to one of the eigenfunctions of ''H''. These vectors are called "state vectors," and using [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1933/dirac.html Dirac's] [[bra-ket notation]] they are represented notationally as | |||
:<math> | \psi \rangle=[c_1 \ c_2 \ \dots \ c_n]^T</math> | |||
In the [[Schrödinger formulation]] of quantum mechanics, this state vector would be represented as | |||
:<math> | \psi \rangle=c_1 \psi_1 + c_2\psi_2+\cdots+c_n\psi_n</math> | |||
===The generalized form=== | |||
Using the abstract concept of a state vector we can define the time-independent Schrödinger equation using the [[bra-ket notation]] of [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1933/dirac.html PAM Dirac] as: | |||
:<math> H |\psi \rangle =E| \psi \rangle</math> | |||
and the time-dependent equation becomes | |||
:<math> H |\psi \rangle =i \hbar \frac{\partial}{\partial t}| \psi \rangle</math> | |||
===Relation to Heisenberg's matrix mechanics=== | |||
About the same time that the Schrödinger equation was developed (in 1926), [http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1932/heisenberg.html Werner Heisenberg] developed (in 1925) a formulation of quantum mechanics based upon the properties of matrices. This formulation can be related to the Schrödinger equation using the generalized bra-ket notation above. The basic idea is to introduce a family of wavefunctions, called ''basis functions'', say |''φ<sub>n</sub>'''''⟩''' , that can represent any wavefunction |''ψ'''''⟩''' as an expansion of the form: | |||
:<math>| \psi \rangle = \sum_n c_n | \phi _n \rangle \ ,</math> | |||
where the coefficients {''c<sub>n</sub>''} are constants that depend upon the basis functions selected. A set of basis functions adequate to this task is called ''complete''. Such basis sets are a generalization of the sine and cosine functions used in [[Fourier series]] to a wider set of functions, a subject sometimes called ''generalized Fourier analysis''.<ref name=Folland> | |||
{{cite book |title=Fourier Analysis and Its Applications |author=GB Folland |url=http://books.google.com/books?id=ix2iCQ-o9x4C&pg=PA77 |pages=p. 77 |isbn=0821847902 |publisher=AMS Bookstore |year=2009 |edition=Reprint of Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole 1992 ed }} | |||
</ref> With such an expansion in hand, the Schrödinger equation can be recast in matrix form in a few steps. Substituting the expansion for the wavefunction into the Schrödinger equation: | |||
:<math>H | \psi \rangle = \sum_n c_n H | \phi _n \rangle = E \sum_n c_n | \phi _n \rangle \ . </math> | |||
The ''ket'' functions complementary to the ''bra'' functions are written as '''⟨'''''φ<sub>n</sub>''|, and the process of multiplying Schrödinger's equation by a complex conjugate basis function and integrating over the space variables of the region under analysis is written as: | |||
:<math>\langle \phi _m |H | \psi \rangle = \sum_n c_n \langle \phi _m |H | \phi _n \rangle =E \sum_n c_n \langle \phi _m | \phi _n \rangle \ . </math> | |||
If now the wavefunction ''ψ'' is identified with a column vector {''c<sub>n</sub>''} and if (as usually can be arranged) the basis functions satisfy the orthonormality condition: | |||
:<math>\langle \phi _m | \phi _n \rangle = \delta_{mn} \ , </math> | |||
where ''δ<sub>nm</sub>'' is the [[Kronecker delta|Kronecker delta function]], then the Schrödinger equation is placed in matrix form as: | |||
:<math> \left[ \ H \ \right] \ \left[\ c\ \right] = E \left[\ c\ \right] \ , </math> | |||
which can be recognized as the matrix equation based upon the Hamiltonian matrix elements | |||
:<math> H_{mn} = \langle \phi _m |H | \phi _n \rangle = \int_{\Omega} \ d \Omega \ \phi^*_m \ H\phi_n \ , </math> | |||
(with ''Ω'' the volume of integration) and the ''ψ''-vector {''c<sub>n</sub>''}. | |||
If this formalism is carried through for all the manipulations of quantum mechanics, the Heisenberg formulation results. It is largely equivalent to the Schrödinger equation formulation, but it is a bit broader mathematically because the formulation is divorced from requirements upon the properties of sets of functions. | |||
==Physical consequences== | |||
===Discrete energy levels=== | |||
''See also'' [[Particle in a box]] | |||
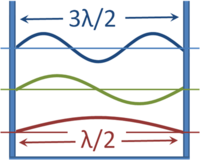
{{Image|Waves in a box.PNG|right|200px|The wavelengths of standing waves in a box that have zero amplitude (nodes) at the walls.}} | |||
For all physical bound states, solutions to the Schrödinger equation yield a number of discrete energy levels and eigenfunctions. This arises in the same manner that the wavelength of a standing wave in an organ pipe is quantized. As shown in the figure, the wavelength of waves in a box that are forced to have zero amplitude at the walls can have only values that are multiples of a half-wavelength. For a sound wave, zero amplitude at the walls is a consequence of the sound being unable to cause vibration of the massive walls. For wavefunctions, zero amplitude at the wall results because the particle cannot penetrate the wall, so the probability of finding the particle inside the wall is zero. Naturally, such walls are an idealization and real walls will permit some slight penetration. | |||
In any event, with the imposition of a condition for nodes at the walls, allowed wavelengths are quantized. Because wavelength ''λ'' (determining the spatial behavior) and frequency ''f'' (determining the time dependence of the wave) are related to the speed ''v'' (at which the wave would propagate if it were free, and not in a box) as ''λ=v/f'', the frequencies also have only discrete values. This classical result that applies to sound waves in a box, for example, in quantum mechanics is applied to wavefunctions in a box, where now energy determines the oscillatory time dependence instead of frequency. Thus, a particle is able to exist in the box with only a set of discrete energy levels. Solutions to the Schrödinger equation for free particles (not confined), however, do result in a continuum of allowed energies: only bound states have their energy quantized. This very close parallel between classical waves and particle wavefunctions led to the name ''wave mechanics'' for the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics. | |||
Experimentally, the discrete nature of energy levels has been verified by the spectra of atoms and molecules: absorption of light energy by an atom or molecule can only take place if the energy of the incident light corresponds to a gap between energy levels. These energy levels are solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the atomic or molecular system, and calculations that solve the Schrödinger equation can provide very accurate electronic, rotational, and vibrational spectra. See [[computational chemistry]]. | |||
===Uncertainty and probability=== | |||
''See also'' [[Measurement in quantum mechanics]] | |||
Even though for a given eigenstate we have an exact value for the energy of the system, it ''does not'' follow that all other [[observable|observable properties]] of the system are also well defined. In fact, the values of two observables whose operators do not [[commutation|commute]] cannot be simultaneously well defined: precision in one observable induces uncertainty in the other (see the [[Heisenberg uncertainty principle]]). This concept is manifest in the popular idea of "Schrödinger's Cat," a cat whose "life status" does not "commute" with a precisely known observable. The uncertainty in the cat's life status means that until the cat is observed and its wavefunction "collapses," the cat is, in a sense, simultaneously alive and dead. The probabilities of the cat being alive and dead are non-zero. | |||
Note that this does ''not'' mean that quantum systems like Schrödinger's Cat are completely and utterly unpredictable. Even though systems that are not in an eigenstate must be described probabilistically, the Schrödinger equation and related quantum eigenvalue equations provide a means to predict the probabilities of observing all possible measurements on the system. Measurement probabilities are known; what cannot be known in advance are the exact results of all possible measurements on the system. | |||
== Solutions of the Schrödinger equation == | |||
Analytical solutions of the time-independent Schrödinger equation can be obtained for a variety of relatively simple conditions. These solutions provide insight into the nature of quantum phenomena and sometimes provide a reasonable approximation of the behavior of more complex systems (e.g., in [[statistical mechanics]], molecular vibrations are often approximated as [[harmonic oscillator (quantum)|harmonic oscillator]]s). A more complex system even is the [[Hydrogen |H<sub>2</sub>]] molecule where only approximations to the solutions can be obtained. Several of the more common analytical solutions include: | |||
* The [[free particle]] | |||
* The [[particle in a box]] | |||
* The [[finite potential well]] | |||
* The [[Delta function potential]] | |||
* The [[particle in a ring]] or [[ring wave guide]] | |||
* The [[particle in a spherically symmetric potential]] | |||
* The [[harmonic oscillator (quantum)|quantum harmonic oscillator]] | |||
* The [[Rigid rotor#The quantum_mechanical linear rigid rotor|linear rigid rotor]] | |||
* The [[Rigid rotor#Schrödinger equation for symmetric top|symmetric top]] | |||
* The [[hydrogen atom]] or [[hydrogen-like atom]] | |||
* The [[particle in a one-dimensional lattice (periodic potential)]] | |||
For many systems, however, there is no analytic solution to the Schrödinger equation. In these cases, one must resort to approximate solutions. Some of the common techniques are: | |||
* [[Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics)|Perturbation theory]] | |||
* The [[variational principle]] underpins many approximate methods (like the popular [[Hartree-Fock]] method which is the basis of the [[post Hartree-Fock]] methods) | |||
* [[Quantum Monte Carlo]] methods | |||
* [[Density functional theory]] | |||
* The [[WKB approximation]] | |||
* [[discrete delta-potential method]] | |||
==References== | |||
<references />[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 16:00, 15 October 2024
The Schrödinger equation is one of the fundamental equations of quantum mechanics and describes the spatial and temporal behavior of quantum-mechanical systems. Austrian physicist Erwin Schrödinger first proposed the equation in early 1926. Actually there are two different equations known as Schrödinger equation: The first is sometimes called the time-dependent, while the second is called the time independent equation, though in reality, it is simply an equation derived from the first using a mathematical technique known as separation of variables. The second one is an eigenvalue equation, written commonly as Hψ = E ψ. The conditions that must be met to enable this separation of variables arise very frequently in chemistry and physics. It should also be noted that the fact that the time independent equation takes the form of a simple eigenvalue problem (thus being more amenable to mathematical analysis) that makes it so useful.
Mathematically, the time-independent Schrödinger equation is an example of an eigenvalue problem whose eigenvectors ψ are called "wavefunctions" or "quantum states" and whose eigenvalues E correspond to energy levels. In many cases these energies can have only certain discrete values, which one expresses by stating that the energies are quantized. Built into the eigenvectors are the probabilities of measuring all values of all physical observables, meaning that a solution of the Schrödinger equation provides a complete physical description of a system. Both Schrödinger equations contain an energy operator H, called a Hamiltonian. In the case that the quantum system has a classical counterpart, the Hamiltonian operator is obtained by replacing the terms in the classical Hamiltonian function by linear operators.
The Schrödinger wave equation
The wavefunction describes a wave of probability, the square of whose amplitude is equal to the probability of finding a particle at position x and time t. But what is the form of Schrödinger's equation, which describes the time and position evolution of the wavefunction? The following is an introduction intended to provide some plausibility for the equation, but of course it is not possible to derive the Schrödinger equation because it is a fundamental postulate of quantum mechanics.
We start by assuming that a beam of particles, like a beam of light, will have a wavefunction of the form
The absolute square |ψ|2 of this function (its probability amplitude) is a constant independent of position and time, which makes sense for a constant beam of particles: there is an equal probability of finding a particle at every point along the beam and any time. Using de Broglie's relations,
- ,
where is Planck's constant divdided by 2π. Based on the functional form of , we see that
Using the classical relationship between kinetic energy and momentum and allowing for a potential,
Substituting for p and E yields the one-dimensional time-dependent Schrödinger wave equation,
When the probability amplitude of the wavefunction is independent of time, it can be shown that energy is constant, and so the equation reduces to
Generalising to several dimensions
In three dimensions, the second derivative becomes the Laplacian:
In spherical coordinates, the spherical definition of the Laplacian gives
Note that the heuristic reasoning in this section makes the form of the Schrödinger equation plausible, but should not be seen as a formal derivation departing from certain axioms. Indeed, it is generally assumed that the (time-dependent) Schrödinger equation itself is one of the central axioms of quantum mechanics.[1]
The time-independent equation
The time-independent S.E. has the form
where
is the Hamiltonian operator. E is the mechanical energy of the particle wave.
H is an example of a quantum-mechanical operator, the Hamiltonian (classical Hamiltonians also exist). It must be a self-adjoint operator because its eigenvalues E are the discrete, real energy levels of the system. Also, the various eigenfunctions must be linearly independent and in fact form a basis for the state space of the system. In other words, the state of any system is reducible to a linear combination of solutions of the Schrödinger equation for that system. The Hamiltonian essentially contains all of the energy "sources" of the system, and its eigenstates describe the possible state of the system entirely.
As an example, consider a particle in a one-dimensional box with infinite potential walls and a finite potential a inside the box. The Hamiltonian of this system is
The first term of the Hamiltonian corresponds to the classical expression for kinetic energy, p2/2m (see above), and the second term is the potential energy as defined. No other sources of energy exist in the system as defined, and so the particle's state must be some linear combination of the eigenstates of H.
A more general formulation
Quantum state vectors
The eigenfunctions of the Schrödinger equation form a basis for the state space of the system. This means that any quantum state can be written as a column vector, each entry of which corresponds to one of the eigenfunctions of H. These vectors are called "state vectors," and using Dirac's bra-ket notation they are represented notationally as
In the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics, this state vector would be represented as
The generalized form
Using the abstract concept of a state vector we can define the time-independent Schrödinger equation using the bra-ket notation of PAM Dirac as:
and the time-dependent equation becomes
Relation to Heisenberg's matrix mechanics
About the same time that the Schrödinger equation was developed (in 1926), Werner Heisenberg developed (in 1925) a formulation of quantum mechanics based upon the properties of matrices. This formulation can be related to the Schrödinger equation using the generalized bra-ket notation above. The basic idea is to introduce a family of wavefunctions, called basis functions, say |φn⟩ , that can represent any wavefunction |ψ⟩ as an expansion of the form:
where the coefficients {cn} are constants that depend upon the basis functions selected. A set of basis functions adequate to this task is called complete. Such basis sets are a generalization of the sine and cosine functions used in Fourier series to a wider set of functions, a subject sometimes called generalized Fourier analysis.[2] With such an expansion in hand, the Schrödinger equation can be recast in matrix form in a few steps. Substituting the expansion for the wavefunction into the Schrödinger equation:
The ket functions complementary to the bra functions are written as ⟨φn|, and the process of multiplying Schrödinger's equation by a complex conjugate basis function and integrating over the space variables of the region under analysis is written as:
If now the wavefunction ψ is identified with a column vector {cn} and if (as usually can be arranged) the basis functions satisfy the orthonormality condition:
where δnm is the Kronecker delta function, then the Schrödinger equation is placed in matrix form as:
which can be recognized as the matrix equation based upon the Hamiltonian matrix elements
(with Ω the volume of integration) and the ψ-vector {cn}.
If this formalism is carried through for all the manipulations of quantum mechanics, the Heisenberg formulation results. It is largely equivalent to the Schrödinger equation formulation, but it is a bit broader mathematically because the formulation is divorced from requirements upon the properties of sets of functions.
Physical consequences
Discrete energy levels
See also Particle in a box
For all physical bound states, solutions to the Schrödinger equation yield a number of discrete energy levels and eigenfunctions. This arises in the same manner that the wavelength of a standing wave in an organ pipe is quantized. As shown in the figure, the wavelength of waves in a box that are forced to have zero amplitude at the walls can have only values that are multiples of a half-wavelength. For a sound wave, zero amplitude at the walls is a consequence of the sound being unable to cause vibration of the massive walls. For wavefunctions, zero amplitude at the wall results because the particle cannot penetrate the wall, so the probability of finding the particle inside the wall is zero. Naturally, such walls are an idealization and real walls will permit some slight penetration.
In any event, with the imposition of a condition for nodes at the walls, allowed wavelengths are quantized. Because wavelength λ (determining the spatial behavior) and frequency f (determining the time dependence of the wave) are related to the speed v (at which the wave would propagate if it were free, and not in a box) as λ=v/f, the frequencies also have only discrete values. This classical result that applies to sound waves in a box, for example, in quantum mechanics is applied to wavefunctions in a box, where now energy determines the oscillatory time dependence instead of frequency. Thus, a particle is able to exist in the box with only a set of discrete energy levels. Solutions to the Schrödinger equation for free particles (not confined), however, do result in a continuum of allowed energies: only bound states have their energy quantized. This very close parallel between classical waves and particle wavefunctions led to the name wave mechanics for the Schrödinger formulation of quantum mechanics.
Experimentally, the discrete nature of energy levels has been verified by the spectra of atoms and molecules: absorption of light energy by an atom or molecule can only take place if the energy of the incident light corresponds to a gap between energy levels. These energy levels are solutions of the Schrödinger equation for the atomic or molecular system, and calculations that solve the Schrödinger equation can provide very accurate electronic, rotational, and vibrational spectra. See computational chemistry.
Uncertainty and probability
See also Measurement in quantum mechanics
Even though for a given eigenstate we have an exact value for the energy of the system, it does not follow that all other observable properties of the system are also well defined. In fact, the values of two observables whose operators do not commute cannot be simultaneously well defined: precision in one observable induces uncertainty in the other (see the Heisenberg uncertainty principle). This concept is manifest in the popular idea of "Schrödinger's Cat," a cat whose "life status" does not "commute" with a precisely known observable. The uncertainty in the cat's life status means that until the cat is observed and its wavefunction "collapses," the cat is, in a sense, simultaneously alive and dead. The probabilities of the cat being alive and dead are non-zero.
Note that this does not mean that quantum systems like Schrödinger's Cat are completely and utterly unpredictable. Even though systems that are not in an eigenstate must be described probabilistically, the Schrödinger equation and related quantum eigenvalue equations provide a means to predict the probabilities of observing all possible measurements on the system. Measurement probabilities are known; what cannot be known in advance are the exact results of all possible measurements on the system.
Solutions of the Schrödinger equation
Analytical solutions of the time-independent Schrödinger equation can be obtained for a variety of relatively simple conditions. These solutions provide insight into the nature of quantum phenomena and sometimes provide a reasonable approximation of the behavior of more complex systems (e.g., in statistical mechanics, molecular vibrations are often approximated as harmonic oscillators). A more complex system even is the H2 molecule where only approximations to the solutions can be obtained. Several of the more common analytical solutions include:
- The free particle
- The particle in a box
- The finite potential well
- The Delta function potential
- The particle in a ring or ring wave guide
- The particle in a spherically symmetric potential
- The quantum harmonic oscillator
- The linear rigid rotor
- The symmetric top
- The hydrogen atom or hydrogen-like atom
- The particle in a one-dimensional lattice (periodic potential)
For many systems, however, there is no analytic solution to the Schrödinger equation. In these cases, one must resort to approximate solutions. Some of the common techniques are:
- Perturbation theory
- The variational principle underpins many approximate methods (like the popular Hartree-Fock method which is the basis of the post Hartree-Fock methods)
- Quantum Monte Carlo methods
- Density functional theory
- The WKB approximation
- discrete delta-potential method
References
- ↑ For example, see Masanori Ohya, Igor Volovich (2011). “§5.11: Seven principles of quantum mechanics”, Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Information and Computation and Its Applications to Nano- and Bio-systems. Springer, pp. 95 ff. ISBN 9400701705. and Mukul Agrawal (4 January, 2002). Axiomatic/ Postulatory quantum mechanics.
- ↑ GB Folland (2009). Fourier Analysis and Its Applications, Reprint of Wadsworth & Brooks/Cole 1992 ed. AMS Bookstore, p. 77. ISBN 0821847902.







![{\displaystyle \ E\psi =[{\frac {p^{2}}{2m}}+V(x)]\psi }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fa003228c924da576f5b7a5e9f72376ecaa49d71)



![{\displaystyle \hbar i{\frac {\partial \psi }{\partial t}}=-{\frac {\hbar ^{2}}{2\mu }}{\frac {1}{r^{2}\sin \theta }}\left[\sin \theta {\frac {\partial }{\partial r}}\left(r^{2}{\frac {\partial \psi }{\partial r}}\right)+{\frac {\partial }{\partial \theta }}\left(\sin \theta {\frac {\partial \psi }{\partial \theta }}\right)+{\frac {1}{\sin \theta }}{\frac {\partial ^{2}\psi }{\partial \phi ^{2}}}\right]+V(r,\theta ,\phi )\psi }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/12bd8b576a48f77d5f532a6a2b317a02a0b4ef2a)




![{\displaystyle |\psi \rangle =[c_{1}\ c_{2}\ \dots \ c_{n}]^{T}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1b76009b3a8b3d37215be519581847232e3c7844)







![{\displaystyle \left[\ H\ \right]\ \left[\ c\ \right]=E\left[\ c\ \right]\ ,}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/00d8c07b67f55d5fd92e8b4fadec773d2476e88f)