South Dakota (U.S. state): Difference between revisions
imported>Drew R. Smith No edit summary |
mNo edit summary |
||
| (11 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{dambigbox|South Dakota (U.S. state)|South Dakota}} | |||
{{TOC|right}} | |||
[[Image:North mid west.jpg|right|350px]] | [[Image:North mid west.jpg|right|350px]] | ||
'''South Dakota''' is one of the constituent states of the [[United States of America]]; it is located on the northern [[Great Plains]] in the north central portion of the United States. Its area is 77,116 sq miles (199,730 square kilometers). Its population (2020 census) was 886,667. The capital is located in [[Pierre, South Dakota|Pierre]]. | |||
South Dakota is | |||
The | ==Physiography (land forms)== | ||
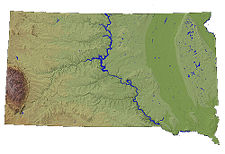
{{Image|South Dakota.jpg|right|225px|USGS shaded relief map of South Dakota}} | |||
The state is divided into three basic physiographical regions. East of the [[Missouri River]], which runs through the central portion of the state from north to south, lies the [[Prairie plains|prairie]] region which was formed by [[glacier|glacial]] deposition and is generally flat with a very slight rise as one travels from east to west. It consists mainly of farmland where the main crop is grains. | |||
West of the Missouri, the land continues to rise, but at a slightly steeper rate, from about 2000 feet above sea level at the Missouri River to over 3000 feet in elevation in the extreme northwest part of the state. This region is part of the [[Great Plains]]. | West of the Missouri, the land continues to rise, but at a slightly steeper rate, from about 2000 feet above sea level at the Missouri River to over 3000 feet in elevation in the extreme northwest part of the state. This region is part of the [[Great Plains]]. This country is significantly dryer than the eastern portion of the state and features mainly rangeland cattle grazing. | ||
The third distinct region is the [[Black Hills]] area in the southwestern part of the state. This is a [[mountain|mountainous]] region, covered by a pine forest, and was sacred to the native peoples of the Great Plains. | The third distinct region is the [[Black Hills]] area in the southwestern part of the state. This is a [[mountain|mountainous]] region, covered by a pine forest, and was sacred to the native peoples of the Great Plains. This region is a center of the state's tourism industry. | ||
==Climate== | |||
Governing the climate in South Dakota is the fact that the state does not lie close to any large bodies of water and thus does not experience the moderating influence of such formations on overall weather patterns. As a result, South Dakota experiences hot summers and cold winters with larger than normal seasonal and diurnal fluctuations in temperature. | Governing the climate in South Dakota is the fact that the state does not lie close to any large bodies of water and thus does not experience the moderating influence of such formations on overall weather patterns. As a result, South Dakota experiences hot summers and cold winters with larger than normal seasonal and diurnal fluctuations in temperature. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 21: | ||
Annual precipitation averges range from 25 inches plus in the southeast portion of the state, decreasing gradually as one goes across the state from the east to the semi-arid west where the average annual preciiptation will be less than 17 inches. | Annual precipitation averges range from 25 inches plus in the southeast portion of the state, decreasing gradually as one goes across the state from the east to the semi-arid west where the average annual preciiptation will be less than 17 inches. | ||
==Economy== | ==Economy== | ||
Agriculture is the leading economic industry in South Dakota. Around 88.5% of the total land area in South Dakota is in farmland. Of the approximately 43.7 million acres of farmland, about 19.1 million acres are in crops and slightly over 23 million acres are devoted to pasteurland. | |||
The state ranks in the top 10 among U.S. states in the production of 25 agricultural commodities. The Sioux Falls stockyards is the largest livestock terminal in the United States. | |||
The | |||
The chief crops are [[corn]], [[soybean]]s, [[oats]], [[wheat]], [[sunflower]]s, and [[sorghum]]. Principal livestock include cattle and calves (3.7 million total), sheep and lambs (305,000), hogs and pigs (1.3 million) and 90,000 milk cows producing about 1.8 billion pounds of [[milk]] per year (all these are 2008 figures). | |||
== | ==History== | ||
The area was first explored by the French in the mid-17th century. Later, in 1803, it was transferred to the United States as part of the [[Louisiana Purchase]]. The next year, the [[Lewis and Clark Expedition]] spent several weeks traversing the future state. In 1861, the Dakota Territory was formed, later split into a northern and southern portion. The two separate portions gained entry into the Union in 1889. | |||
The | |||
== | ==Attractions== | ||
Tourism is an important industry in South Dakota with the Black Hills Containing the main attractions. [[Mount Rushmore]] is the most famous landmark in the state, but here, or nearby, one will also find the [[Badlands National Park]] and [[Wind Cave National Park]]. | |||
Another, different kind of attraction, is the annual [[Sturgis]] motorcycle rally which attracts several hundred thousand visitors each year. | |||
== | ==See also== | ||
[[United States of America/Catalogs/States and Territories|U.S. States and Territories]] | |||
== | ==References== | ||
<references> | |||
</references>[[Category:Suggestion Bot Tag]] | |||
Latest revision as of 11:01, 20 October 2024
South Dakota is one of the constituent states of the United States of America; it is located on the northern Great Plains in the north central portion of the United States. Its area is 77,116 sq miles (199,730 square kilometers). Its population (2020 census) was 886,667. The capital is located in Pierre.
Physiography (land forms)
The state is divided into three basic physiographical regions. East of the Missouri River, which runs through the central portion of the state from north to south, lies the prairie region which was formed by glacial deposition and is generally flat with a very slight rise as one travels from east to west. It consists mainly of farmland where the main crop is grains.
West of the Missouri, the land continues to rise, but at a slightly steeper rate, from about 2000 feet above sea level at the Missouri River to over 3000 feet in elevation in the extreme northwest part of the state. This region is part of the Great Plains. This country is significantly dryer than the eastern portion of the state and features mainly rangeland cattle grazing.
The third distinct region is the Black Hills area in the southwestern part of the state. This is a mountainous region, covered by a pine forest, and was sacred to the native peoples of the Great Plains. This region is a center of the state's tourism industry.
Climate
Governing the climate in South Dakota is the fact that the state does not lie close to any large bodies of water and thus does not experience the moderating influence of such formations on overall weather patterns. As a result, South Dakota experiences hot summers and cold winters with larger than normal seasonal and diurnal fluctuations in temperature.
During the peak summer months, mean daily maximum temperatures will be in the mid to upper 80s (degrees F) while during the winter months mean daily lows will be in the teens or single digits (degrees F).
Annual precipitation averges range from 25 inches plus in the southeast portion of the state, decreasing gradually as one goes across the state from the east to the semi-arid west where the average annual preciiptation will be less than 17 inches.
Economy
Agriculture is the leading economic industry in South Dakota. Around 88.5% of the total land area in South Dakota is in farmland. Of the approximately 43.7 million acres of farmland, about 19.1 million acres are in crops and slightly over 23 million acres are devoted to pasteurland.
The state ranks in the top 10 among U.S. states in the production of 25 agricultural commodities. The Sioux Falls stockyards is the largest livestock terminal in the United States.
The chief crops are corn, soybeans, oats, wheat, sunflowers, and sorghum. Principal livestock include cattle and calves (3.7 million total), sheep and lambs (305,000), hogs and pigs (1.3 million) and 90,000 milk cows producing about 1.8 billion pounds of milk per year (all these are 2008 figures).
History
The area was first explored by the French in the mid-17th century. Later, in 1803, it was transferred to the United States as part of the Louisiana Purchase. The next year, the Lewis and Clark Expedition spent several weeks traversing the future state. In 1861, the Dakota Territory was formed, later split into a northern and southern portion. The two separate portions gained entry into the Union in 1889.
Attractions
Tourism is an important industry in South Dakota with the Black Hills Containing the main attractions. Mount Rushmore is the most famous landmark in the state, but here, or nearby, one will also find the Badlands National Park and Wind Cave National Park.
Another, different kind of attraction, is the annual Sturgis motorcycle rally which attracts several hundred thousand visitors each year.