Sinkhole (geology): Difference between revisions
George Swan (talk | contribs) (first draft) |
George Swan (talk | contribs) ({{subpages}}) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
[[File:Mosul Dam sinkhole.jpg | left | thumb | Sinkholes can appear without warning.]] | [[File:Mosul Dam sinkhole.jpg | left | thumb | Sinkholes can appear without warning.]] | ||
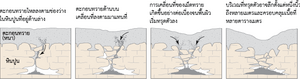
[[File:หลุมยุบที่เกิดจากการพังทลายของชั้นดินที่ปกคลุม (Cover-collapse sinkholes).png | thumb]] | [[File:หลุมยุบที่เกิดจากการพังทลายของชั้นดินที่ปกคลุม (Cover-collapse sinkholes).png | thumb]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:42, 31 January 2024
| The metadata subpage is missing. You can start it via filling in this form or by following the instructions that come up after clicking on the [show] link to the right. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sinkhole is a term from geography.
Sinkholes form when erosion in the flow of water, underground, undermines the integrity of the surface.[1][2][3][4]
References
- ↑ Williams, Paul (2004). “Dolines”, Encyclopedia of Caves and Karst Science (in en). Taylor & Francis, 628–642. ISBN 978-1-57958-399-6.
- ↑ Kohl, Martin (2001). Subsidence and sinkholes in East Tennessee. A field guide to holes in the ground. State of Tennessee.
- ↑ (2009) The Dictionary of Physical Geography, 3rd. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1444313161.
- ↑ Monroe, Watson Hiner (1970). "A glossary of Karst terminology". U.S. Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 1899-K. DOI:10.3133/wsp1899k. Research Blogging.