Pythagorean theorem: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>Michael Hardy (expanded on the statement) |
imported>Aleksander Stos m (-template) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
The "legs" are the two sides of the triangle that meet at a right angle. The hypotenuse is the other side—the side opposite the right angle. | The "legs" are the two sides of the triangle that meet at a right angle. The hypotenuse is the other side—the side opposite the right angle. | ||
[[Category: Mathematics Workgroup]] | [[Category: Mathematics Workgroup]] | ||
[[Category: CZ Live]] | [[Category: CZ Live]] | ||
Revision as of 08:38, 13 October 2007

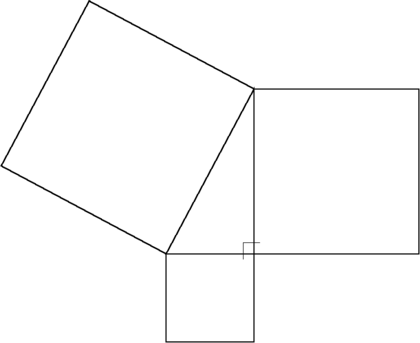
The Pythagorean theorem: The sum of the areas of the two squares on the legs (the sides that meet at a right angle) equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle).
In Euclidean geometry, the Pythagorean theorem states that:
- The sum of the areas of the squares on the legs of a right triangle equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse.
The "legs" are the two sides of the triangle that meet at a right angle. The hypotenuse is the other side—the side opposite the right angle.