Sun: Difference between revisions
imported>Thomas Simmons (added reference section) |
imported>Thomas Simmons No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
The '''sun''' is a middle-sized [[main sequence]] [[star]], more specifically a [[yellow dwarf]], which has eight recognized [[planets]], three [[dwarf planets]] and myriad [[asteroids]] revolving around it. It mainly consist of [[hydrogen]], which it converts to [[helium]] through a process of [[nuclear fusion]], providing the heat and light that allowed [[life]] to form here on our planet, [[Earth]]. The sun is about 93 million miles, or about eight [[light minutes]], away from Earth. | The '''sun''' is a middle-sized [[main sequence]] [[star]], more specifically a [[yellow dwarf]], which has eight recognized [[planets]], three [[dwarf planets]] and myriad [[asteroids]] revolving around it. It mainly consist of [[hydrogen]], which it converts to [[helium]] through a process of [[nuclear fusion]], providing the heat and light that allowed [[life]] to form here on our planet, [[Earth]]. The sun is about 93 million miles, or about eight [[light minutes]], away from Earth. | ||
{{Image|391872main Filament Aheadzm.jpg|right|450px|Sun's eruption.<ref>Sun's eruption[http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/stereo/multimedia/filament_eruption.html]</ref>}} | |||
As a star, there is nothing unusual about it. But the sun is more important to people than any other star. Without the heat and light of the sun, there would be no life on earth. It is the only star of which we can clearly observe the surface. For this reason, scientists study it to learn about stars much farther away. The visible surface of the sun consists of hot gases that give off light and heat. Only about one two-billionth of sun's light and heat reaches the earth. The rest of the sun's light and heat is lost in space. | As a star, there is nothing unusual about it. But the sun is more important to people than any other star. Without the heat and light of the sun, there would be no life on earth. It is the only star of which we can clearly observe the surface. For this reason, scientists study it to learn about stars much farther away. The visible surface of the sun consists of hot gases that give off light and heat. Only about one two-billionth of sun's light and heat reaches the earth. The rest of the sun's light and heat is lost in space. | ||
Revision as of 22:00, 4 March 2010
The sun is a middle-sized main sequence star, more specifically a yellow dwarf, which has eight recognized planets, three dwarf planets and myriad asteroids revolving around it. It mainly consist of hydrogen, which it converts to helium through a process of nuclear fusion, providing the heat and light that allowed life to form here on our planet, Earth. The sun is about 93 million miles, or about eight light minutes, away from Earth.
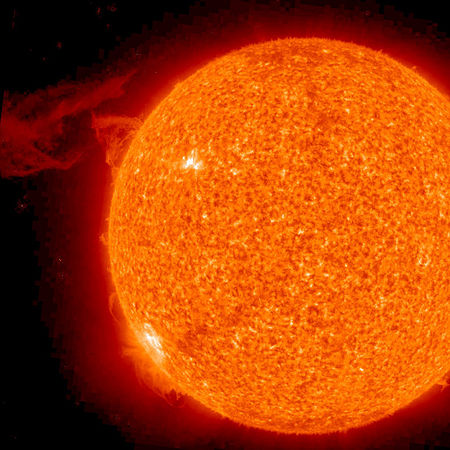
As a star, there is nothing unusual about it. But the sun is more important to people than any other star. Without the heat and light of the sun, there would be no life on earth. It is the only star of which we can clearly observe the surface. For this reason, scientists study it to learn about stars much farther away. The visible surface of the sun consists of hot gases that give off light and heat. Only about one two-billionth of sun's light and heat reaches the earth. The rest of the sun's light and heat is lost in space.
Distance from the earth: Shortest about 147,100,000 kilometers; Greatest about 152,100,000 kilometers; Mean about 150 million kilometers. Sunlight takes about 8 minutes and 20 seconds to reach the earth, traveling at 299,792 km/s.
Diameter: 1,392,000 km
Volume 1,300,000 times that of earth.
Mass 99.8% mass of solar system; about 333,000 times that of the earth
Temperature Center- about 15,000,000° C; Surface about 5500° C. That represents cooling by a factor of more than 2,000 at the surface, to a temperature almost twice the temperature at which iron boils (iron boiling point: 3,000° C (5,432° F))[2]
Rotation period About 1 month
Revolution period in the Milky Way: About 225 million years
Chemical makeup: Hydrogen, about 75%; helium, about 25%; at least 70 other elements make up the remaining 1 to 2 percent
Density Convection zone - about 1/10 that of water
Radiative zone - about equal to that of water
Core - about 100 times that of water