Diazinon: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk mNo edit summary |
imported>Gareth Leng |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
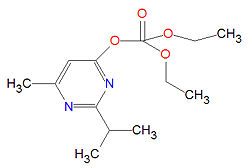
'''Diazinon''', IUPAC name '''O,O-Diethyl 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinylphosphorothioate''', is a pesticide developed by Geigy in the 1950s used to control insects, ticks and nematodes on many crops including fruit trees, vegatables, forage and pasture crops and ornamental plants. | '''Diazinon''', IUPAC name '''O,O-Diethyl 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinylphosphorothioate''', is a pesticide developed by Geigy in the 1950s used to control insects, ticks and nematodes on many crops including fruit trees, vegatables, forage and pasture crops and ornamental plants. | ||
== | ==Toxicity == | ||
Diazinon is toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin adsorption. Because it is an [[acetylcholinesterase]] inhibitor, intoxication is similar to exposure to nerve agents. Long term use of the product, especially among commercial gardeners, can lead to permenant nerve damage. In some cases of exposure, [[atropine]] may be indicated. | Diazinon is toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin adsorption. Because it is an [[acetylcholinesterase]] inhibitor, intoxication is similar to exposure to nerve agents. Long term use of the product, especially among commercial gardeners, can lead to permenant nerve damage. In some cases of exposure, [[atropine]] may be indicated. | ||
==References== | |||
<references/> | |||
== other names == | == other names == | ||
Revision as of 07:56, 14 March 2009
Diazinon, IUPAC name O,O-Diethyl 2-isopropyl-6-methyl-4-pyrimidinylphosphorothioate, is a pesticide developed by Geigy in the 1950s used to control insects, ticks and nematodes on many crops including fruit trees, vegatables, forage and pasture crops and ornamental plants.
Toxicity
Diazinon is toxic by inhalation, ingestion and skin adsorption. Because it is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, intoxication is similar to exposure to nerve agents. Long term use of the product, especially among commercial gardeners, can lead to permenant nerve damage. In some cases of exposure, atropine may be indicated.
References
other names
This chemical is sold under dozens of trade names and many more trivial names, listed below.
Trade names
- Acinon
- Bazinon
- Cekuzinon
- Danol
- Devizinon
- Diacidol
- Diagran
- Diaphos
- Diazain
- Diazate
- Diazichem
- Diazinobomeed
- Diazol
- Dizalux
- Diazudin
- Fordizon
- Forsudin
- Forwazinon
- Geater
- Hezudin
- Laidan
- Metazon
- Nemazone
- Newsibon
- Vazinon
- Vibasu
- Vitanon
- Wopro-diazinon
- Woprozinol
trivial names
- AG-500
- AI3-19507
- Alfa-tox Antigal
- BRN 0273790
- Bassadinon
- Basudin
- Bazanon
- Bazuden
- CCRIS 204
- Caswell No. 342
- Ciazinon
- Compass
- Cooper's Flystrike Powder
- Dacutox
- Dassitox
- Dazzel
- Delzinon
- Diazajet
- Diazide
- Diazinon
- Diazinone
- Diazitol
- Diazol
- Dicid
- Dimpilato
- Dimpylat
- Dimpylate
- Disonex
- Dizictol
- Dizinil
- Dizinon
- Drawizon
- Dyzol
- Ektoband
- Evict
- Exodin
- Flytrol
- G 24480
- G 301
- G-24480
- Galesan
- Garden Tox
- Geigy 24480
- HSDB 303
- Hi-Yield Imported Fire Ant Killer
- KFM Blowfly Dressing
- Kayazinon
- Kayazol
- Kleen-Dok
- Knox Out 2FM
- Knox Out Yellow Jacket Contorl
- Knox-out
- Meodinon
- Neocidol
- Neodinon
- Nipsan
- Nucidol
- OMS 469
- Oleodiazinon
- Optimizer
- Ortho Diazinon Ultra
- PT 265
- Sarolex
- Spectracide
- Srolex
- Terminator
- Topclip 40
- Topclip Blue
- Topclip Blue Shield