Spironolactone: Difference between revisions
imported>Caesar Schinas m (Bot: Update image code) |
imported>Robert Badgett No edit summary |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{{Image|Spironolactone DEVolk.jpg|right|150px|Spironolactone, an aldosterone antagonist.}} | {{Image|Spironolactone DEVolk.jpg|right|150px|Spironolactone, an aldosterone antagonist.}} | ||
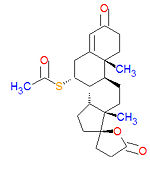
'''Spironolactone''' is an [[aldosterone]] antagonist used to treat [[edema]] associated with [[ | '''Spironolactone''' is an [[aldosterone]] antagonist used to treat [[edema]] associated with congestive [[heart failure]], [[nephrotic syndrome]] or [[hepatic cirrhosis]]. Although it can also be used treat [[hirsutism]] and [[acne]] by effecting the [[endocrine system]], such use can lead to adverse side effects. It is also used to treat [[hypertension]]. | ||
Its IUPAC name is S-[(7R,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-3,5'-dioxospiro[2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15, | Its IUPAC name is S-[(7R,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-3,5'-dioxospiro[2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15, | ||
16-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-17,2'-oxolane]-7-yl] ethanethioate. | 16-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-17,2'-oxolane]-7-yl] ethanethioate. | ||
== | == Trade names == | ||
<div class= style="-moz-column-count:3; column-count:3;"> | |||
*Abbolactone | *Abbolactone | ||
*Acelat | *Acelat | ||
| Line 59: | Line 60: | ||
*Verospirone | *Verospirone | ||
*Verospirone Opianin | *Verospirone Opianin | ||
*Xenalon | *Xenalon | ||
</div> | |||
==Clinical use== | |||
===Heart failure=== | |||
Spironolactone can help patients who have New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IV [[heart failure]] and had a left ventricular ejection fraction of no more than 35%.<ref name="pmid10471456">{{cite journal| author=Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A et al.| title=The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 1999 | volume= 341 | issue= 10 | pages= 709-17 | pmid=10471456 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=10471456 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref>, although it is both used incorrectly<ref name="pmid15295047">{{cite journal| author=Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Lee DS, Kopp A, Austin PC, Laupacis A et al.| title=Rates of hyperkalemia after publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study. | journal=N Engl J Med | year= 2004 | volume= 351 | issue= 6 | pages= 543-51 | pmid=15295047 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=15295047 | doi=10.1056/NEJMoa040135 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref> and at the same time is underutilized<ref name="pmid19843900">{{cite journal| author=Albert NM, Yancy CW, Liang L, Zhao X, Hernandez AF, Peterson ED et al.| title=Use of aldosterone antagonists in heart failure. | journal=JAMA | year= 2009 | volume= 302 | issue= 15 | pages= 1658-65 | pmid=19843900 | |||
| url=http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/eutils/elink.fcgi?dbfrom=pubmed&retmode=ref&cmd=prlinks&id=19843900 | doi=10.1001/jama.2009.1493 }} <!--Formatted by http://sumsearch.uthscsa.edu/cite/--></ref>. | |||
===Hypertension=== | |||
Resistant [[hypertension]] is characterized by volume expansion and abnormalities of the [[renin-angiotensin system]] with high [[aldosterone]] and [[cortisol]] with low [[renin]] levels in the plasma<ref name="pmid19487712">{{cite journal |author=Sowers JR, Whaley-Connell A, Epstein M |title=Narrative review: the emerging clinical implications of the role of aldosterone in the metabolic syndrome and resistant hypertension |journal=Ann. Intern. Med. |volume=150 |issue=11 |pages=776–83 |year=2009 |month=June |pmid=19487712 |doi= |url=http://www.annals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=19487712 |issn=}}</ref><ref name="pmid18541823">{{cite journal |author=Gaddam KK, Nishizaka MK, Pratt-Ubunama MN, ''et al'' |title=Characterization of resistant hypertension: association between resistant hypertension, aldosterone, and persistent intravascular volume expansion |journal=Arch. Intern. Med. |volume=168 |issue=11 |pages=1159–64 |year=2008 |month=June |pmid=18541823 |doi=10.1001/archinte.168.11.1159 |url=http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18541823 |issn=}}</ref> in spite of many patients taking thiazide [[diuretic]]s.<ref name="pmid18541823"/>{ This suggests that high [[corticotropin]] may contribute<ref name="pmid18541823"/>, in some cases due to an abnormal [[cytochrome P-450]] 3A5 allele that may reduce metabolism of [[cortisol]] and [[corticosterone]] (a precursor of [[aldosterone]]).<ref name="pmid12754175">{{cite journal |author=Givens RC, Lin YS, Dowling AL, ''et al'' |title=CYP3A5 genotype predicts renal CYP3A activity and blood pressure in healthy adults |journal=J. Appl. Physiol. |volume=95 |issue=3 |pages=1297–300 |year=2003 |month=September |pmid=12754175 |doi=10.1152/japplphysiol.00322.2003 |url=http://jap.physiology.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12754175 |issn=}}</ref> Resistent hypertension is also associated with insulin resistance.<ref name="pmid3299096">{{cite journal |author=Ferrannini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, ''et al'' |title=Insulin resistance in essential hypertension |journal=N. Engl. J. Med. |volume=317 |issue=6 |pages=350–7 |year=1987 |month=August |pmid=3299096 |doi= |url= |issn=}}</ref> | |||
In an unblinded, uncontrolled extension of the ASCOT [[randomized controlled trial]], spironolactone 25-50 mg per day as a fourth medication for [[hypertension]] reduced the blood pressure by 21.9/9.5. This result was not affected by whether one of the first three medications included a [[diuretic]].<ref name="pmid17309946">{{cite journal |author=Chapman N, Dobson J, Wilson S, ''et al'' |title=Effect of spironolactone on blood pressure in subjects with resistant hypertension |journal=Hypertension |volume=49 |issue=4 |pages=839–45 |year=2007 |month=April |pmid=17309946 |doi=10.1161/01.HYP.0000259805.18468.8c |url=http://hyper.ahajournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17309946 |issn=}}</ref> A second study study, also uncontrolled, corroborated the role of spironolactone.<ref name="pmid14573330">{{cite journal |author=Nishizaka MK, Zaman MA, Calhoun DA |title=Efficacy of low-dose spironolactone in subjects with resistant hypertension |journal=Am. J. Hypertens. |volume=16 |issue=11 Pt 1 |pages=925–30 |year=2003 |month=November |pmid=14573330 |doi=10.1016/S0895-7061(03)01032-X |url= |issn=}}</ref> In this study, 54% of patients were African-American, 45% had primary hyperaldosteronism. | |||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
{{CZMed}} | {{CZMed}} | ||
==references== | |||
<references/> | |||
Revision as of 18:39, 22 October 2009
Spironolactone is an aldosterone antagonist used to treat edema associated with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome or hepatic cirrhosis. Although it can also be used treat hirsutism and acne by effecting the endocrine system, such use can lead to adverse side effects. It is also used to treat hypertension. Its IUPAC name is S-[(7R,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,17R)-10,13-dimethyl-3,5'-dioxospiro[2,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15, 16-decahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-17,2'-oxolane]-7-yl] ethanethioate.
Trade names
- Abbolactone
- Acelat
- Aldace
- Aldactazide
- Aldactide
- Aldactone
- Aldactone A
- Alderon
- Aldopur
- Almatol
- Altex
- Aquareduct
- Deverol
- Diatensec
- Dira
- Duraspiron
- Espironolactona [INN-Spanish]
- Euteberol
- Lacalmin
- Lacdene
- Laractone
- Melarcon
- Nefurofan
- Osyrol
- SNL
- Sagisal
- Sincomen
- Spiresis
- Spiretic
- Spiridon
- Spiro-Tablinen
- Spiroctan
- Spiroctanie
- Spiroderm
- Spirolactone
- Spirolakton
- Spirolang
- Spirolone
- Spirone
- Spironocompren
- Spironolactone A
- Spironolactone [BAN:INN:JAN]
- Spironolactonum [INN-Latin]
- Spironolattone [DCIT]
- Sprioderm
- Supra-puren
- Suracton
- Uractone
- Urusonin
- Verospiron
- Verospirone
- Verospirone Opianin
- Xenalon
Clinical use
Heart failure
Spironolactone can help patients who have New York Heart Association (NYHA) class IV heart failure and had a left ventricular ejection fraction of no more than 35%.[1], although it is both used incorrectly[2] and at the same time is underutilized[3].
Hypertension
Resistant hypertension is characterized by volume expansion and abnormalities of the renin-angiotensin system with high aldosterone and cortisol with low renin levels in the plasma[4][5] in spite of many patients taking thiazide diuretics.[5]{ This suggests that high corticotropin may contribute[5], in some cases due to an abnormal cytochrome P-450 3A5 allele that may reduce metabolism of cortisol and corticosterone (a precursor of aldosterone).[6] Resistent hypertension is also associated with insulin resistance.[7]
In an unblinded, uncontrolled extension of the ASCOT randomized controlled trial, spironolactone 25-50 mg per day as a fourth medication for hypertension reduced the blood pressure by 21.9/9.5. This result was not affected by whether one of the first three medications included a diuretic.[8] A second study study, also uncontrolled, corroborated the role of spironolactone.[9] In this study, 54% of patients were African-American, 45% had primary hyperaldosteronism.
External links
The most up-to-date information about Spironolactone and other drugs can be found at the following sites.
- Spironolactone - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Spironolactone - Drug information for consumers from MedlinePlus (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Spironolactone - Detailed information from DrugBank.
references
- ↑ Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A et al. (1999). "The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators.". N Engl J Med 341 (10): 709-17. PMID 10471456.
- ↑ Juurlink DN, Mamdani MM, Lee DS, Kopp A, Austin PC, Laupacis A et al. (2004). "Rates of hyperkalemia after publication of the Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study.". N Engl J Med 351 (6): 543-51. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa040135. PMID 15295047. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Albert NM, Yancy CW, Liang L, Zhao X, Hernandez AF, Peterson ED et al. (2009). "Use of aldosterone antagonists in heart failure.". JAMA 302 (15): 1658-65. DOI:10.1001/jama.2009.1493. PMID 19843900. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Sowers JR, Whaley-Connell A, Epstein M (June 2009). "Narrative review: the emerging clinical implications of the role of aldosterone in the metabolic syndrome and resistant hypertension". Ann. Intern. Med. 150 (11): 776–83. PMID 19487712. [e]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Gaddam KK, Nishizaka MK, Pratt-Ubunama MN, et al (June 2008). "Characterization of resistant hypertension: association between resistant hypertension, aldosterone, and persistent intravascular volume expansion". Arch. Intern. Med. 168 (11): 1159–64. DOI:10.1001/archinte.168.11.1159. PMID 18541823. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Givens RC, Lin YS, Dowling AL, et al (September 2003). "CYP3A5 genotype predicts renal CYP3A activity and blood pressure in healthy adults". J. Appl. Physiol. 95 (3): 1297–300. DOI:10.1152/japplphysiol.00322.2003. PMID 12754175. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Ferrannini E, Buzzigoli G, Bonadonna R, et al (August 1987). "Insulin resistance in essential hypertension". N. Engl. J. Med. 317 (6): 350–7. PMID 3299096. [e]
- ↑ Chapman N, Dobson J, Wilson S, et al (April 2007). "Effect of spironolactone on blood pressure in subjects with resistant hypertension". Hypertension 49 (4): 839–45. DOI:10.1161/01.HYP.0000259805.18468.8c. PMID 17309946. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Nishizaka MK, Zaman MA, Calhoun DA (November 2003). "Efficacy of low-dose spironolactone in subjects with resistant hypertension". Am. J. Hypertens. 16 (11 Pt 1): 925–30. DOI:10.1016/S0895-7061(03)01032-X. PMID 14573330. Research Blogging.