Pregabalin: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk (structure pic of pregabalin, gabapentin and GABA) |
imported>David E. Volk (chemical info) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
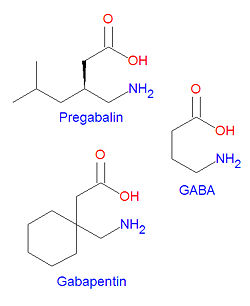
'''Pregabalin''' is structurally similar to [[gabapentin]]. Tt is also similar to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid ([[GABA]]), and although it does not act on GABA receptors, it may increase the "density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport".<ref name="DailyMed">{{DailyMed}}</ref> It is approved by the for neuropathic pain associated with [[diabetic neuropathy|diabetic peripheral neuropathy]], postherpetic neuralgia adjunctive therapy for adult patients with partial onset [[seizure]]s, and [[fibromyalgia]].<ref name="DailyMed">{{DailyMed}}</ref> | '''Pregabalin''' is structurally similar to [[gabapentin]]. Tt is also similar to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid ([[GABA]]), and although it does not act on GABA receptors, it may increase the "density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport".<ref name="DailyMed">{{DailyMed}}</ref> It is approved by the for neuropathic pain associated with [[diabetic neuropathy|diabetic peripheral neuropathy]], postherpetic neuralgia adjunctive therapy for adult patients with partial onset [[seizure]]s, and [[fibromyalgia]].<ref name="DailyMed">{{DailyMed}}</ref> | ||
== chemistry == | |||
The IUPAC chemical name for pregabalin is (S)-(+)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Its chemical formula is C<sub>8</sub>H<sub>17</sub>NO<sub>2</sub> giving it a molecular mass of 159.23 g/mol. It is both an [[amine]] and a [[carboxylic acid]]. | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 29 February 2008
Pregabalin is structurally similar to gabapentin. Tt is also similar to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and although it does not act on GABA receptors, it may increase the "density of GABA transporter protein and increases the rate of functional GABA transport".[1] It is approved by the for neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia adjunctive therapy for adult patients with partial onset seizures, and fibromyalgia.[1]
chemistry
The IUPAC chemical name for pregabalin is (S)-(+)-3-(aminomethyl)-5-methylhexanoic acid. Its chemical formula is C8H17NO2 giving it a molecular mass of 159.23 g/mol. It is both an amine and a carboxylic acid.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Pregabalin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).