Sine rule: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Paul Wormer (New page: In trigonometry, the '''sine rule''' states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of a triangle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the opposite sides, see Fig.1 [[Image:Sine...) |
imported>Paul Wormer No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | |||
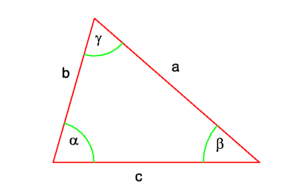
In [[trigonometry]], the '''sine rule''' states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of a triangle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the opposite sides, see Fig.1 | In [[trigonometry]], the '''sine rule''' states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of a triangle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the opposite sides, see Fig.1 | ||
[[Image:Sine rule.png|right|thumb|300px|Fig. 1. Sine rule: sinα:sinβ:sinγ=a:b:c]] | [[Image:Sine rule.png|right|thumb|300px|Fig. 1. Sine rule: sinα:sinβ:sinγ=a:b:c]] | ||
Revision as of 04:09, 18 October 2008
In trigonometry, the sine rule states that the ratio of the sines of the angles of a triangle is equal to the ratio of the lengths of the opposite sides, see Fig.1