Great Depression in the United States/Tutorials: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>Nick Gardner |
imported>Nick Gardner |
||
| Line 231: | Line 231: | ||
==Output and Unemployment== | ==Output and Unemployment== | ||
(1935-39 = 100 | :(Output: 1935-39 = 100) | ||
:(Unemployment: - excluding WPA employees - % of civilian labour force) | |||
:::::{| class="wikitable" | :::::{| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 238: | Line 239: | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1931 | !style="background:#eeeeee;" |1931 | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1933 | !style="background:#eeeeee;" |1933 | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1934 | |||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1935 | |||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1936 | |||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1937 | !style="background:#eeeeee;" |1937 | ||
!style="background:#eeeeee;" |1938 | |||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"|Industrial Production | |align="center"|Industrial Production | ||
| Line 244: | Line 249: | ||
|align="center"|75 | |align="center"|75 | ||
|align="center"|69 | |align="center"|69 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|align="center"|112 | |align="center"|112 | ||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
|align="center"|Unemployment | |align="center"|Unemployment | ||
|align="center"|3.1 | |align="center"|3.1 | ||
|align="center"|16.1 | |align="center"|16.1 | ||
|align="center"| | |align="center"|20.6 | ||
|align="center"| | |align="center"|16.0 | ||
|align="center"|14.2 | |||
|align="center"|9.9 | |||
|align="center"|9.1 | |||
|align="center"|12.5 | |||
|} | |} | ||
:::Source: ''Historical Statistics'' | :::Source: ''Historical Statistics'' | ||
Revision as of 05:13, 5 February 2009
- Statistics of the Depression
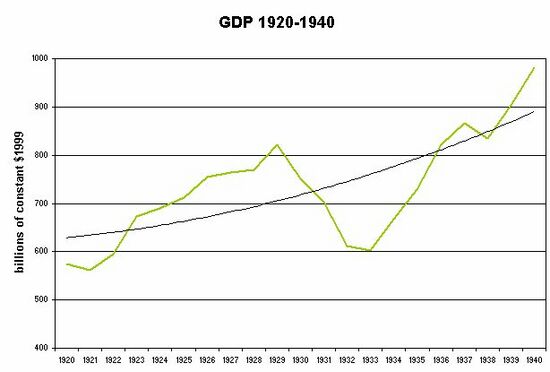
GDP Trend

Chart 1: GDP annual pattern and long-term trend, 1920-40, in billions of constant dollars[1]
- ↑ based on data in Susan Carter, ed. Historical Statistics of the US: Millennial Edition (2006) series Ca9
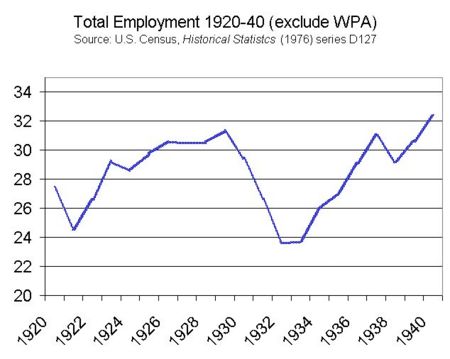
Employment Trend
Expenditure levels
- (billions of 1929 dollars)
1928 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 Gross National Product 98.5 104.4 95.1 89.5 76.4 74.2 80.8 91.4 100.9 109.1 Consumer Spending 74.8 79.0 74.7 72.2 66.0 64.6 68.0 72.3 79.7 82.6 Gross Investment 14.5 16.2 10.5 6.8 0.8 0.3 1.8 8.8 9.3 14.6 Construction 9.8 8.7 6.4 4.5 2.4 1.9 2.0 2.8 3.9 4.6
- Source: Kendrik 1961 [1]
Price Indexes
(1947-49 = 100)
1928 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 Wholesale Prices 62.9 61.9 56.1 47.4 42.1 42.8 48.7 52.0 52.5 56.1 Consumer Prices 73.3 73.3 71.4 65.0 58.4 55.3 57.2 58.7 59.3 61.4
- Source Historical Statistics[1]
Money Supply
(billions of dollars)
1928 1929 1930 1931 1932 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 M1 26.2 26.4 25.4 23.6 20.5 19.4 21.5 25.5 29.2 30.3 M2 46.1 46.2 45.2 41.7 34.6 30.8 33.3 38.4 42.8 45.0 High-powered money 7.1 7.1 6.9 7.3 7.8 8.2 9.1 10.7 12.2 13.4
- Source: Friedman and Schwartz [1]
Fiscal Stance
- (Full employment deficit - see the Glossary)
| 1929 | 1930 | 1931 | 1932 | 1933 | 1934 | 1935 | 1936 | 1937 | 1938 | 1939 | 1940 | 1941 | 1942 | 1943 | 1944 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deficit % of potential GDP | -0.5 | -1.5 | -1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 15 | 25 |
Sources: De Long [1] and Krugman [2]
Output and Unemployment
- (Output: 1935-39 = 100)
- (Unemployment: - excluding WPA employees - % of civilian labour force)
1929 1931 1933 1934 1935 1936 1937 1938 Industrial Production 109 75 69 112 Unemployment 3.1 16.1 20.6 16.0 14.2 9.9 9.1 12.5
- Source: Historical Statistics
Bank Failures
1930 1931 1932 1933 Percent of operating banks[2] 5.6 10.5 7.8 12.9