User:John R. Brews/Devices: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
imported>John R. Brews |
imported>John R. Brews No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC|right}} | |||
==Devices== | ==Devices== | ||
{{Gallery-mixed | {{Gallery-mixed | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
|FCC Fermi surface.PNG|Fermi surface in '''k'''-space for a nearly filled band in the face-centered cubic lattice | |FCC Fermi surface.PNG|Fermi surface in '''k'''-space for a nearly filled band in the face-centered cubic lattice | ||
}} | }} | ||
==More devices== | |||
{{Gallery-mixed | {{Gallery-mixed | ||
|caption=More devices | |caption=More devices | ||
Revision as of 09:02, 15 July 2011
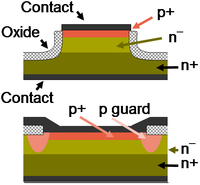
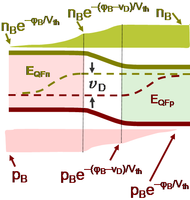
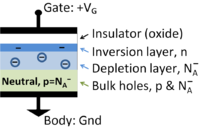
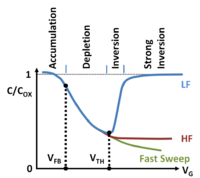
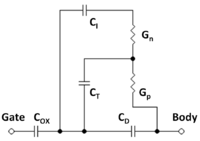
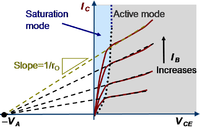
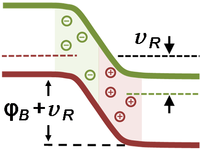
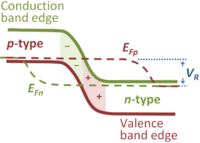
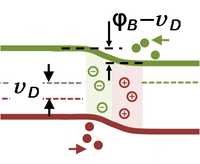
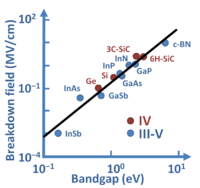
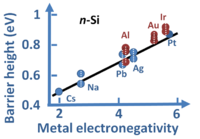
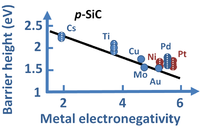
Devices
| Devices | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
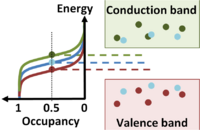
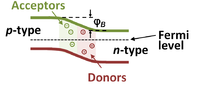
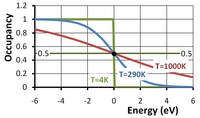
More devices
| More devices | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||