United States Navy: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz (→Ships) |
imported>John Leach m (John Leach moved page U.S. Navy to United States Navy over redirect: consistency) |
(No difference)
| |
Revision as of 15:01, 8 October 2019
The U.S. Navy is a branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is charged with sea operations in both international and American waters.
"The mission of the Navy is to maintain, train and equip combat-ready Naval forces capable of winning wars, deterring aggression and maintaining freedom of the seas."[1]
Missions
Its combat functions include anti-surface warfare (ASuW) against ships, anti-submarine warfare (ASW), anti-air warfare (AAW), land attack, littoral warfare, naval gunfire support, mine warfare, amphibious warfare, and Naval Special Warfare.
It has an extremely sophisticated support structure for its combat units. Japanese admirals, after the Second World War, cited "fast carrier operations", which implied the "seatrain" to resupply and maintain the carrier task forces at sea, as one of the three fundamental things that beat Japan. The others were submarine operations and island-hopping. Logistics, therefore, cannot be overstressed.
Also as a result of WWII experience, the US Navy tends to be compulsive about safety and damage control, with a considerable record of saving battle-damaged ships that might well be lost in other navies. Recruit training has been changed recently, so a stressful and realistic damage control exercise is the culminating event of the course.
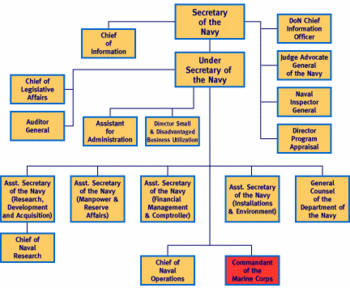
Current organization
There are several major parts to the Navy:
- Civilian leadership in the Department of the Navy
- Shore establishment
- Operating forces
In turn, the operating forces are split into those deployed in the field, which report to the National Command Authority via the Unified Combatant Commanders. Forces that are in training, maintenance, readiness for deployment, or doctrinal development report, through the shore establishment, to the Chief of Naval Operations.
Command, control, communications, computers
- See also: U.S. Navy/Catalogs/Electronics
The modern navy is extremely network-centric. At the strategic, operational, and logistic level, its systems tie into the Global Information Grid (GIG) of the U.S. Department of Defense. Fleet level operations connect both to the GIG and to the Global Command and Control System-Maritime, as well as theater-level systems for the Unified Combatant Commands, such as the Theater Battle Management Core System.
These high-level systems are linked through the Defense Information Systems Network and a variety of satellite communications systems. The Fleet Broadcast System and MILSATCOM are older satellites; some of the new ones, heavily used by the Navy, include the UHF Follow-On, Global Broadcast Service and Wideband Global Satellite.
At the tactical level, there is a high degree of interoperability among all the military services, sharing the Joint Tactical Information Distribution System. The AEGIS battle management system is the key information system for anti-air warfare (AAW), ballistic missile defense (BMD) and land attack, and interoperates with national BMD networks. Cooperative Engagement Capability is an extension of AEGIS, which lets tactical decisions, down to the level of firing and guiding missiles, be distributed among multiple ships. The Naval Fire Control System controls naval gunfire support in cooperation with artillery ashore.
Ships
- See also: U.S. Navy/Catalogs/Ship classes
Vessels at sea usually operate in groups. Carrier Strike Groups have the greatest combat capabilities. Amphibious Ready Groups carry Marine units, and may be combined with non-carrier warships to become Expeditionary Strike Groups. Submarines are attached to some of these units, but also conduct considerable independent operations.
The major operational ship types are:
- Aircraft carriers of the Nimitz-class, with the new CVN-21 class building
- Cruisers of the Ticonderoga-class
- Destroyers of the Burke-class; construction of the Zumwalt-class has been capped in favor of more Burkes and more research
- Ocean escorts, called frigates, of the Oliver Hazard Perry-class
- Littoral Combat Ships, still experimental
- Amphibious warfare ships, including:
- Wasp-class [r]: The largest amphibious warfare ships in the United States Navy, which carry a Marine Expeditionary Unit and supporting aircraft [e]
- San Antonio-class [r]: Used in amphibious warfare, a class of Landing Platform Dock ships of the United States Navy, with some in commission and some under construction; they displace 24,900 tons and will replace the Austin-class (LPD-4) [e]
- Austin-class [r]: Predecessor of the San Antonio-class of Landing Platform Dock (LPD) ships, which have both a well deck for landing craft and a flight deck for vertical takeoff aircraft and helicopters; fully loaded, they displace 16,914 tons; the Trenton and Cleveland classes are part of the Austins but sometimes listed as separate classes [e]
- Prepositioning ship [r]: Add brief definition or description
- Attack submarines of the Los Angeles-class and (capped) Seawolf-class; new Virginia-class boats are under construction
- Ballistic missile submarines of the Ohio-class. Some have been converted for cruise missile and naval special warfare
- Logistic vessels
- See also: U.S. Navy/Catalogs/Aircraft types
When both its carrier-capable and shore-based aircraft, as well as helicopters, are counted, the United States Navy operates one of the world's largest air forces.
On carriers, the main aircraft are:
- F-18 Super Hornet multirole fighters
- EF-18 Growler electronic warfare aircraft
- E-2 Hawkeye airborne early warning
Helicopters serve both on carriers and other surface warships. While they were primarily H-60 helicopter family, there were a wide range of types, which are being reconciled to two for other than amphibious warfare
- MH-60S Knighthawk, utility and mine countermeasures, replacing CH-46 Sea Knight utility/Marine, HH-60H Rescue Hawk, MH-53E Sea Dragon mine clearing.
- MH-60R, probably called yet another Seahawk, replacing the SH-60B and SH-60F in the multimission ASW/ASuW.
The CH-53 Sea Stallion is being retained for heavy lift in amphibious operations, but the CH-46 is being replaced by the tilt-rotor V-22 Osprey.
Land-based aircraft of note include:
- P-3 Orion maritime patrol aircraft, to be replaced by the P-8 Poseidon
- E-6 TACAMO strategic command and control aircraft, jointly operated with the United States Air Force
History
Created in 1775 with the immediate concern of the American Revolution, the U.S. Navy were disbanded in 1783 and the privateers went back to the merchant trade. The needs of international commerce, however, soon drove the requirement for a standing navy, more than it did an army.
The War Department was created in 1789 and handled naval affairs. The Federalist Party, especially under John Adams favored the Navy and created the cabinet-level Department of the Navy in 1798. The Marines originated in 1775, when two battalions of men were raised for continental service; it was deactivated in 1783. The Marine Corps was reactivated by Congress on July 11, 1798, within the new Navy Department. Benjamin Stoddert was the first secretary and directed operations during the "Quasi-War", the undeclared naval war with France (1798-1800).
The Algerian War (1815), suppression of West Indian pirates (1816-29), and antislavery patrols (1820-50) provided training for the Mexican-American War of 1846-48.
In 1815 the Board of Navy Commissioners, consisting of three senior officers, was created to provide technical advice to the department regarding naval technology, naval operations being excluded from its purview. In 1842 an organization of technical bureaus was instituted, including bureaus for the Navy Yards and Docks; Construction, Equipment, and Repairs; Provisions and Clothing; Ordnance and Hydrography; and Medicine and Surgery.
The Navy professionalized the officer corps, with the Naval Academy (1854). It experimented with steam propulsion and sponsored overseas explorations, notably the Pacific expedition (1838-1842) of Lieutenant Charles Wilkes.