Hetacillin: Difference between revisions
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk m (→External links) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
== External links == | == External links == | ||
* {{DailyMed}} | * {{DailyMed}} | ||
* | * {{MedMaster}} | ||
* {{DrugBank}} | |||
Revision as of 12:53, 5 March 2008
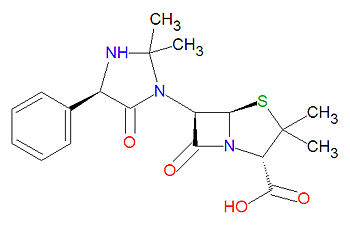
Hetacillin is a penicillin-like, beta-lactam based antibiotic prodrug used to treat infections, usually from gram-positive bacteria.
Mechanism of action
Hetacillin is a prodrug with no antibacterial activity, but it is metabolized into the antibiotic ampicillin. Hetacillin is prepared by reacting ampicillin with acetone because ampicillin is much less stable towards ring-opening reactions. Once converted to ampicillin, the ampicillin interferes with the final stage of cell wall synthesis by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, leading to autolysis of the bacteria by autolysin enzymes.
Chemistry
It is a beta-lactam structure, and its chemical name is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(4R)-2,2-dimethyl-5-oxo-4-phenylimidazolidin-1-yl]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid. Its chemical formula is C19H23N3O4S (MW = 389.4686 g/mol).
External links
- Hetacillin - FDA approved drug information (drug label) from DailyMed (U.S. National Library of Medicine).
- Template:MedMaster
- Template:DrugBank