Docosahexaenoic acid: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search

imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
imported>David E. Volk No edit summary |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
|width=450px | |width=450px | ||
|molname=docosahexaenoic acid | |molname=docosahexaenoic acid | ||
|synonyms= cervonic acid, | |synonyms= '''cervonic acid''', '''cervonate''' | ||
|molformula= C<sub>22</sub>H<sub>32</sub>O<sub>2</sub> | |molformula= C<sub>22</sub>H<sub>32</sub>O<sub>2</sub> | ||
|molmass= 328. | |molmass= 328.48831 | ||
|uses=natural nutrient | |uses=natural nutrient | ||
|properties=omega-3 fatty acid | |properties=omega-3 fatty acid | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
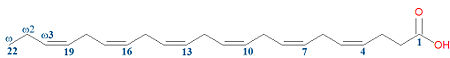
'''Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)''', more correctly called '''docosa-4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z-hexaenoic acid''', is a naturally occuring [[omega-3]] fatty acid. It is a fatty acid that contains a linear chain of twenty-two carbon atoms, with double bonds occuring at six positions, all with the cis configuration. It is called an omega-3 fatty acid because from the aliphatic end of the molecule, always referred to as the omega carbon, the first double bond occurs at carbon 19, the omega-3 carbon. | '''Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)''', more correctly called '''docosa-4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z-hexaenoic acid''', is a naturally occuring [[omega-3]] fatty acid. It is a fatty acid that contains a linear chain of twenty-two carbon atoms, with double bonds occuring at six positions, all with the cis configuration. It is called an omega-3 fatty acid because from the aliphatic end of the molecule, always referred to as the omega carbon, the first double bond occurs at carbon 19, the omega-3 carbon. Like other omega-3 fatty acids, it can be found in fish. | ||
== Synonyms == | == Synonyms == | ||
Revision as of 16:05, 7 April 2008
|
| |||||||
| docosahexaenoic acid | |||||||
| |||||||
| Uses: | natural nutrient | ||||||
| Properties: | omega-3 fatty acid | ||||||
| Hazards: | |||||||
| |||||||
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), more correctly called docosa-4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z-hexaenoic acid, is a naturally occuring omega-3 fatty acid. It is a fatty acid that contains a linear chain of twenty-two carbon atoms, with double bonds occuring at six positions, all with the cis configuration. It is called an omega-3 fatty acid because from the aliphatic end of the molecule, always referred to as the omega carbon, the first double bond occurs at carbon 19, the omega-3 carbon. Like other omega-3 fatty acids, it can be found in fish.
Synonyms
- 4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid
- cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid
- (4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic acid (IUPAC)
- all Z-docosahexaenoic acid
- all cis-docosahexaenoic acid
- Cervonic acid
- Cervonate