Drug treatments for obesity: Difference between revisions
imported>Gareth Leng |
imported>Gareth Leng (→CART: moved to new article) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
[[Ephedrine]] is a [[sympathomimetic]] amine, which acts as a stimulant and appetite suppressant. It has mild efficacy as a weight loss drug and when combined synergistically with caffeine, it have been shown to be very effective for long-term weight loss. <ref>Diepvens K ''et al.''(2007) Obesity and thermogenesis related to the consumption of caffeine, ephedrine, capsaicin, and green tea. ''Am J Physiol'' 292:R77-85</ref> However, there are problems associated with the fact both drugs act to increase the outputs of the [[sympathetic nervous system]]. These include a rise in blood pressure, [[palpitations]], insomnia and [[tremor]]. | [[Ephedrine]] is a [[sympathomimetic]] amine, which acts as a stimulant and appetite suppressant. It has mild efficacy as a weight loss drug and when combined synergistically with caffeine, it have been shown to be very effective for long-term weight loss. <ref>Diepvens K ''et al.''(2007) Obesity and thermogenesis related to the consumption of caffeine, ephedrine, capsaicin, and green tea. ''Am J Physiol'' 292:R77-85</ref> However, there are problems associated with the fact both drugs act to increase the outputs of the [[sympathetic nervous system]]. These include a rise in blood pressure, [[palpitations]], insomnia and [[tremor]]. | ||
==Conclusion== | ==Conclusion== | ||
Revision as of 05:33, 15 December 2010
Current drug treatments for obesity are relatively ineffective. Whilst many treatments are successful in promoting weight loss in the short term; long term maintenance is a key problem that has yet to be overcome. With the ever inceasing prevalence of obesity in the developed, and now developing world, it is an integral concern to epidemiologists, policy makers and scientists looking to treat obesity. Here we explain the basic mechanisms of action underlying the current pharmacological treatments and also the avenues of development that any future drugs may take.
Serotonin & Noradrenaline Related Drugs
Method of Action
Sibutramine is a drug, originally used in the treatment of depression, [1] which is now used to help obese and overweight patients lose weight, and along with Orlistat, in 2008 was the only drug licensed for use in the UK. [2] It acts within the hypothalamus by preventing reuptake of both noradrenaline and serotonin. [3][4] This inhibition causes the patient increased feelings of satiety, a decreased appetite, and a corresponding reduced intake of food which results in weight loss. [5] Some studies have shown that sibutramine may increase thermogenesis and as such, contribute to weight loss, but there have also been other studies in which no such effects were shown, and it seems that this action contributes in, at most a minor way to weight loss. It is also thought that sibutramine may effect levels of the hormones leptin and ghrelin, as well as central neuropeptide Y (NPY), and proopiomelanocortin (POMC) mRNA. Sibutramine treatment differs to orlistat in relation to leptin, as, when using sibutramine, transfer of leptin into the brain is maintained or even increased during weight loss which does not happen when using orlistat.
Side-effects
One of the major side-effects of sibutramine therapy is the increase, in a dose-dependent manner, of both blood pressure and heart rate. [1][3] An obese patient is likely to already have elevated blood pressure and heart rate, and as a result, if an obese patient is taking sibutramine, it is important to check these levels on a regular basis to make sure they are not too highly elevated. [2] Patients with hypertension and/or cardiovascular disease are strongly advised against taking the drug due to these adverse effects. As well as these side-effects, sibutramine can also on occasion cause the patient to suffer from a dry mouth, constipation and insomnia. [6] Any adolescents taking sibutramine should be regularly checked for a possible increase in suicidal thoughts, as it acts in a similar way to anti-depressants by preventing noradrenaline and serotonin uptake. [3]
This drug has now been withdrawn in the UK for fears of it increasing the likelihood of heart attacks and strokes
Endocannabinoids
CB1 receptors
.
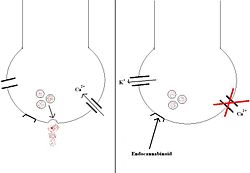
Endocannabinoids are endogenously-made compounds that act on cannabinoid receptors within the central nervous system (CB1) and peripheral tissues (CB2). The CB1 receptors are G-protein coupled receptors, located on the plasma membranes of neurones in specific regions of the brain, including the hippocampus; the cerebellum; the hypothalamus; and various dopaminergic 'reward' pathways. When a cannabinoid compound binds to the CB1 receptor, it has two main actions: 1) calcium entry to the cell is inhibited by blocking calcium channels 2) potassium channels are activated, causing potassium to exit and hyperpolarise the cell The net effect is that neurotransmitter release is inhibited, as shown on the right.
Rimonabant
CB1 receptor antagonists, in particular rimonabant, have been used in tackling obesity. The link between appetite and the CB1 receptors is unclear, but is likely to be particularly important in those receptors in the hypothalamus. Mice genetically engineered to be deficient in CB-1 receptors are resistant to diet-induced obesity, and clinical trials of rimonabant have demonstrated significant weight loss in obese subjects when combined with a reduction in calorie intake, as well as an improvement the ratio of "good" (HDL) to "bad" (LDL) cholesterol.[7]
However, a major issue in using CB1 antagonists is the incidence of psychiatric problems, in particular, depression; unfortunately several suicides occurred during clinical trials. [3] As a result, the FDA has not approved the use of rimonabant in the USA. The European Medicines Agency (EMEA) has recommended the marketing authorisation of rimonabant be suspended across the EU, and consequently the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) has withdrawn its guidance for the use of the drug.[8]
Peripheral Drugs
Orlistat
‘Peripherally acting anti-obesity drugs’ work by reducing the calorie intake from food, or by altering the metabolism of it in the gastrointestinal system (gut). Currently only one drug of this kind is approved for use globally - Orlistat (Xenicol), and it works by inhibiting the enzyme lipase that breaks down fat in the gut, meaning that the fat cannot be absorbed from food, and instead it is excreted out of the body. [9] This can reduce the amount of fat absorbed from the gut by 30%, causing a decreased calorie intake and therefore weight loss. The weight loss from taking this medication is between 5-10% on average. [10] As well as weight loss, Orlistat improves several other cardiovascular risk-factors. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) and triglyceride levels were reduced by more than expected for the weight loss, as well as blood pressure, waist circumference and lipids being reduced. [11] Some research also suggests that Orlistat reduces fasting glucose and HbA1c levels in type 2 diabetics by more than predicted for the weight loss, with suggested methods including increased insulin sensitivity and glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion in the small intestine. Orlistat also reduces the risk of type 2 diabetes in obese subjects. [5]
However, this drug has side-effects. Oily-spotting, flatulence, abdominal cramps, faecal urgency/incontinence and liquid stools are the common adverse effects of Orlistat, due to an increase of fat in the gut and stools. [9] These side-effects are reported to only be experienced during the early stages, “but they subside as patients learn to use the drug”. [3] Orlistat also prevents some absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (vitamins A,E,D and K), and so patients are recommended to take supplements. The drug does not have any systemic side-effects as it is contained in the gut, however it does affect the absorption of acyclovir (an antiviral), so they shouldn’t be used at the same time. [3]
In 2001 the NICE issued a press release on guidance for Orlistat use, and it states that it is cost effective to the NHS. [12]
Amylin
As well as pharmaceutical drugs that work in the periphery to cause weight loss, there are also intrinsic chemicals produced in the body (hormones) that when released cause satiety. One example is amylin, which is a hormone secreted along with insulin from the pancreas in response to a meal, causing you to feel full, therefore regulating your meal size. An amylin analogue, Pramlintide, is currently being looked into as a potential anti-obesity therapy, with it already being used in diabetics. [11]
Glucagon-like peptide-1
Another example is glucagon-like peptide-1, which is released from the gut during eating, and relays satiety information to the brain via the vagus nerve. This is not yet approved, however, for obesity treatment. [11]
Others
Another hormone secreted in the gut, peptide YY, could also be a potential for use, along with pancreatic polypeptide (PP) – both of which decrease appetite. Small-scale trials in a peptide called Oxyntomodulin have also been promising, with larger trials waiting to be preformed. [11]
Other Drug Therapies
Off Label Uses of Prescribed Medication
Some drugs are not primarily indicated for use as weight loss therapies but may be effective in this role. Below is a list of drugs and the evidence to support or disprove their usefulness as anti-obesity agents.
Anti-Diabetic Medication
Metformin & Acarbose
In patients with type II diabetes, there is evidence to support the use of metformin and acarbose as weight loss agents. [13] The role of metformin in stabilising blood glucose levels has been shown to aid weight loss and also - perhaps by another mechanism - to reduce appetite. [14] Acarbose is believed to simply slow nutrient digestion and interact with glucagon-like peptide-1 to aid a slight weight loss. In contrast, patients without type II diabetes will not benefit to the same extent although trials have shown minor improvements. [10] In The Diabetes Prevention Program, the weight loss achieved in a group of non-diabetic patients taking metformin was approximately half of that of a 'lifestyle modification' group, and the mean weight loss was only slightly higher than in the placebo group. [15]. Acarbose is of even less use in this context, neither helping with weight loss or with maintaining a healthy weight.
Liraglutide
Liraglutide is a long-acting analogue of glucagon-like peptide-1. Effects are a result of mimicking endogenous GLP-1 (see above), with the addition of a reduction in food consumption. It has recently been shown to be effective in non-diabetic groups[16], resulting in significant weight loss compared to a placebo and orlistat. Liraglutide also reduced fasting lipids and mean systolic blood pressure. With regard to long-term weight maintenance, further studies are still required.
Diuretics
Diuretics, cause an increase in fluid loss (e.g. by means of hypo-absorption in the nephron), and as such have no role in weight loss by reducing body fat stores. They are abused, however as means of a 'quick-fix' pseudo-weight loss, giving the impression of a reduction in body weight whilst in reality, they are simply causing dehydration. They have been used for some time in the sporting world, particularly boxing, for boxers to 'make the weight' or simply to reduce likelihood of other drugs being found by urine testing. [17] They are also used by women suffering from pre-menstrual water retention. [18]
Thyroid Hormones
One potential method of tackling obesity is the use of thyroid hormone mimetics. Thyroid hormones (T3, T4) act on the thyroid hormone receptors (THR) to elevate the body’s metabolic rate, increasing oxygen consumption leading to an increased use of fat for energy production. However the hormones also have stimulatory effects on the heart rate, causing tachycardia and dangerous arrhythmias, as well as raising the metabolism of muscle protein and promoting bone turnover. [19]
Thyroid hormone mimetics – compounds with similar effects on the fat metabolism without causing any of the unwanted cardiac symptoms – have been developed and tested on animals. One of these named GC-1, an agonist for the thyroid hormone receptor beta 1 (THRB1) has been shown to have minimal effects on the cardiac muscle, whilst stimulating fat metabolism in rats. GC-1 has also been shown to reduce body weight in primates, though this may not specifically be fat loss.
GC-1 and KB2155 (another THRB1 agonist) have been tested in human trials, with no report of weight loss, though this could be due to insufficient doses or the minimal trial period. It remains to be seen what benefit these drugs could offer in humans, both on obesity and on other metabolic conditions. [20]
Caffeine & Ephedrine
Caffeine is a stimulant belonging to the xanthine class of drugs. It is an attractive pharmacological agent for consideration in the context of helping people to lose weight, not only because of its wide global availability, social acceptability and price. Caffeine increases thermogenesis in humans and reducing appetite, but as a long-term weight loss agent it shows decreased efficacy. [21] This is believed to be because of the tolerance (upregulation of adenosine receptors) that develops to caffeine usage.
Ephedrine is a sympathomimetic amine, which acts as a stimulant and appetite suppressant. It has mild efficacy as a weight loss drug and when combined synergistically with caffeine, it have been shown to be very effective for long-term weight loss. [22] However, there are problems associated with the fact both drugs act to increase the outputs of the sympathetic nervous system. These include a rise in blood pressure, palpitations, insomnia and tremor.
Conclusion
Obesity levels are increasing at a dramatic rate, and this brings with it a plethora of other associated health conditions. This presents a huge burden to the NHS, both today and in years to come. There are few drugs currently available aimed specifically to help reduce body weight and of these, a large number have prohibitive side-effects. There are a small group of drugs which have the additional benefit of causing weight loss along with their main action (e.g. metformin), but these have been shown to be ineffective purely as anti-obesity medications. Many possibilities are being looked into as a successful method of weight loss treatment, with particular focus on endogenous hormones, and the role they play in diet control, and weight maintenance in humans. A more holistic approach may be the solution, taking into account the role of societal and the psychological issues surrounding excessive weight gain, rather than purely approaching the topic from a pharmacological perspective.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Woo T (2009) Pharmacotherapy and surgery treatment for the severely obese adolescent. J Paediatric Health Care 23:206-12
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Rang H et al.(2007) Pharmacology. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier. 417-8
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Bray G (2008) Lifestyle and pharmacological approaches to weight loss: efficacy and safety. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:S81–8
- ↑ Tziomalos K et al. (2009) The use of sibutramine in the management of obesity and related disorders: An update. Vascular Health and Risk Management 5:441-52
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Coutinho W (2009) The first decade of sibutramine and orlistat: a reappraisal of their expanding roles in the treatment of obesity and associated conditions. Arquivos Brasileiros De Endocrinologia E Metabologia 53:262-70
- ↑ Boon NA et al.(2006) Davidson's Principles & Practice of Medicine 111-117
- ↑ Kintscher U (2008) The cardiometabolic drug rimonabant: after 2 years of RIO-Europe and STRADIVARIUS. European Heart J
- ↑ NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: Guidance: Obesity - rimonabant (withdrawn) (2008), Viewed 15 October 2009. Available http://www.nice.org.uk/TA144
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Elangbam CS (2009) Current strategies in the development of anti-obesity drugs and their safety concerns. Vet Pathol 26:10-24
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Desilets AR et al.(2008). Role of metformin for weight management in patients without type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacotherapy 42:817-26
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Zanella M, Filho F (2009) Emerging drugs for obesity therapy. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metab 53:271-80
- ↑ NHS National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence: Press release (2001), Viewed 7 October 2009,
- ↑ Siraj ES] (2003) Is there a role for metformin or acarbose as a weight-loss agent in the absence of diabetes? Cleve Clin J Med 70:702-4
- ↑ Hauptman J et al. (2000) Orlistat in the Long-term Treatment of Obesity in Primary Care Settings. Arch Fam Med 9:160–7
- ↑ Knowler WC et al. (2002) Reduction in the incidence of type 2 diabetes with lifestyle intervention or metformin. N Engl J Med 346:393-403
- ↑ Astrup A et al. (2009). "Effects of liraglutide in the treatment of obesity: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.". Lancet 374: 1606-16. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61375-1. PMID 19853906. Research Blogging.
- ↑ Bulik CM (1992). Abuse of drugs associated with eating disorders. J Subst Abuse 4:69-90.
- ↑ Wagner JC (1991). Enhancement of athletic performance with drugs. An overview. Sports Med 12:250-65
- ↑ Rang H et al. (2007) Pharmacology. Churchill Livingstone, Elsevier. pp 441-4
- ↑ Baxter JD, Webb P (2009) Thyroid hormone mimetics: potential applications in atherosclerosis, obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:308-20l
- ↑ Greenway FL (2001) The safety and efficacy of pharmaceutical and herbal caffeine and ephedrine use as a weight loss agent. Obes Rev 2:199-211.
- ↑ Diepvens K et al.(2007) Obesity and thermogenesis related to the consumption of caffeine, ephedrine, capsaicin, and green tea. Am J Physiol 292:R77-85