Ibuprofen: Difference between revisions
imported>Howard C. Berkowitz No edit summary |
imported>Meg Taylor No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{subpages}} | {{subpages}} | ||
{{Image|Ibuprofen.png|right|200px|'''Ibuprofen'''}} | {{Image|Ibuprofen.png|right|200px|'''Ibuprofen'''}} | ||
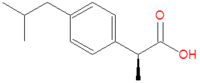
'''Ibuprofen''' is an analgesic drug and a member of the class of drugs | '''Ibuprofen''' is an analgesic drug and a member of the class of drugs referred to as [[non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent|non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs]] (NSAIDS). It is thought to be a nonselective [[cyclooxygenase]] (COX) inhibitor, and, like other NSAIDS, may lead to discomfort and ulceration of the [[gastrointestinal tract]]. | ||
== Chemistry == | == Chemistry == | ||
Revision as of 22:45, 15 September 2013
Ibuprofen is an analgesic drug and a member of the class of drugs referred to as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS). It is thought to be a nonselective cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitor, and, like other NSAIDS, may lead to discomfort and ulceration of the gastrointestinal tract.
Chemistry
Along with naproxen, it is the NSAID class called the propionic acid derivatives. The form used as a drug is formally the (S)-(+)-Ibuprofen isomer, although it may be sold as a racemic mixture. It is also called other names, including (2S)-2-[4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl]propionic acid, (S)-(+)-4-Isobutyl-alpha-methylphenylacetic acid, and (S)-(+)-2-(4-Isobutylphenyl)propionic acid.
It has a molecular formula of C13H18O2 and a molecular mass of 206.28 grams/mole.