Egypt
| Arab Republic of Egypt | |
|---|---|
| |
| National anthem | Bilady, Bilady, Bilady |
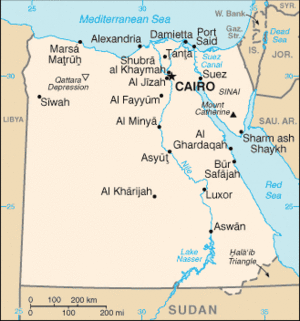
| Capital | Cairo |
| Official language | Arabic |
| Government type | Republic |
| President | Interim military rule; Mohamed Hussein Tantawi interim head of state |
| Prime Minister | Ahmed Shafik |
| Area | 1,001,450 km² 386,660 mi² |
| Population | 80,335,036 (2007 estimate) |
| Population density | 74/km² (120) 192 mi² |
| HDI | 0.708 (medium) (112) (2007) |
| Currency | Egyptian pound (EGP) |
| Time zone | EET (UTC+2) Summer:EEST (UTC+3) |
| Country codes | Internet TLD : .eg Calling code : ++20 |
Egypt (Arabic: مصر, Misr; Coptic: Χημι, Khēmi), or officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country mainly in the north-eastern corner of Africa. It borders Sudan to the south, Libya to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Red Sea, the Gaza Strip and Israel to the east, where its Sinai Peninsula forms part of Asia. Egypt's official language is Arabic, and its capital and largest city is Cairo.
Recent Egyptian history has been defined by the 30-year rule of Hosni Mubarak, who was President from 1981 to 2011, wielding very strong political powers. Until 2011, there was little organised political opposition, and the Egyptian military was a strong force in supporting the regime.[1] Mubarak was forced from office after weeks of civil demonstrations, with an interim military regime taking over. Currently the interim head of state is the leader of the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces, Mohamed Hussein Tantawi.[2]
Egypt has been inhabited for the past ten thousand years, and its ancient culture was one of the most important in antiquity, producing monuments like the Sphinx and pyramids. It was an important province in the Roman and Byzantine empires. In the 7th century, it was invaded by the Arabs, and thereafter became a center of Arab and Islamic scholarship. Today it is arguably the political and cultural center of the Arab world.
Geography
Egypt is mostly desert, and almost never receives rainfall. The Nile river flows through the center of the country, and 97% of Egypt's population lives within a few miles of its fertile banks, where all farming takes place. Egypt is historically divided into Upper Egypt, the upstream areas of the Nile in the south of the country, and Lower Egypt in the north which includes the Nile Delta, which contains Eqypt's best farmland.
History
Egypt was first united around 3200 BC, by the Wild Bull Lord, Menes. The civilization created lasted for the next 3,000 years until 332 BC, when it was conquered by Alexander the Great. This era produced many magnificent temples and monuments, and of course the pyramids. After Alexander, the Greek Ptolemy dynasty, descended from one of Alexander's generals, ruled until 30 BC, when Egypt fell to the Romans. It remained a province of the Romans, and later the Byzantines, until 639, when the Arabs conquered it. Egypt was an integral part of the Umayyad Caliphate and the later Abbasid Cailphate. In 969, it was conquered by the Fatimids, who built the city of Cairo to be their capital. In 1171, the Ayyubids under Saladin came to power. They were replaced by the Mamluks in 1250, who lasted until 1517, when the Ottomans took over. In the 19th century, Egypt was gradually taken over by the British, who made it a de facto part of their empire, though it was only legally annexed in 1914. Egypt gained independence in 1922, though Britain retained influence behind the scenes. In 1952, the monarchy was overthrown in a coup, and after a brief struggle, Gamel Abdul Nasser came to power. He believed that all Arab countries should be united into one, and unified Egypt with Syria for a brief time, though the union (called the United Arab Republic) failed. He also opposed Israel, leading to his defeat in the Six Day War. In 1970, he was succeeded by Anwar Sadat, who made peace with Israel in the Camp David Accords. After Sadat's assassination, his Vice-President Hosni Mubarak took office.

Demonstrators in Egypt protesting against the 30-year rule of Hosni Mubarak climb on top of an army tank in Tahrir Square, Cairo.
After over 30 years of Mubarak in power, early 2011 saw the strongest anti-government demonstrations in Egypt's recent history, with thousands of people on the streets of Cairo to protest against his rule. Tahrir ('Liberation') Square in central Cairo became a focal point for protests, with demonstrators fighting pro-Mubarak groups in running battles that involved rocks being thrown, several deaths, hundreds of injuries and, at one stage, men loyal to the regime charging into the crowds on horseback and camels.[3] On 11th February 2011, after two weeks of demonstrations in which the army had largely declined to intervene, Mubarak was forced to step down in favour of an interim military leadership,[4] which subsequently suspended the constitution and dissolved Parliament pending reforms and fresh elections.[5]
Demography
Egypt's population is almost entirely Arabic-speaking. About 90% of the population is Muslim; most of the rest are Coptic Christians.
Politics

Cairo, which stands on the banks of the River Nile, is the capital of Egypt.
Egypt is a republic, which until 2011 had a constitution that provided for a democratic system with separation of powers and civil liberties; in reality, the country had long been run on a one-party basis. From 2011 until 2012, a military junta took power, suspending the constitution pending a new one and dissolving Parliament. The Supreme Council of the Armed Forces claimed interim status only, but upheld a state of emergency that had lasted virtually unbroken since 1967, and under which many constitutional freedoms were suspended. Until 2011 the then-ruling President, Hosni Mubarak, and the National Democratic Party maintained a tight grip on political power, and human rights violations were widespread. In 2012, Mohamed Morsi of the Muslim Brotherhood's Freedom and Justice Party won the first democractic election since Mubarak was deposed, but a year later was himself ousted in a military coup following widespread protests.[6] Pro-democracy groups continue to await true reform.
Economy
Egypt's economy is historically agricultural, although it now imports food. Egypt has small oil reserves, especially natural gas, which it exports to Jordan and Israel. Cotton exports and tourism are important. Egypt is still a developing country, and a large percentage of the population lives in poverty.
Footnotes
- ↑ New York Times: 'Succession gives army a stiff test in Egypt.' September 11, 2010.
- ↑ According to the Egyptian Constitution, the Speaker of the lower house of the Egyptian Parliament becomes head of state for an interim period in the event that the office becomes vacant; however, in an apparent breach of the constitution, one of the final acts of Hosni Mubarak was to transfer power to the military high command. See BBC News, 'Egypt's Mubarak resigns as leader', 11th February 2011.
- ↑ Coverage of the events in Cairo and across Egypt were covered by the BBC, CNN, Al-Jazeera and other major news organisations.
- ↑ BBC News: 'Egypt's Mubarak resigns as leader'. 11th February 2011.
- ↑ BBC News: 'Egyptian military dissolves parliament'. 13th February 2011.
- ↑ BBC News: 'Army ousts Egypt's President Morsi'. 3rd July 2013.
