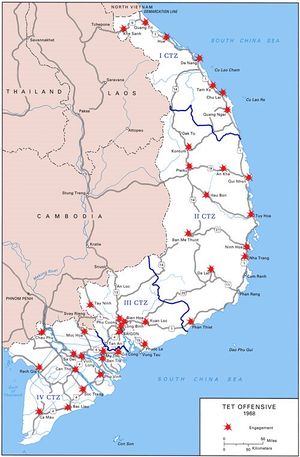
Tet Offensive
On January 31, 1968, during the traditional cease-fire of the Tet holiday, Communist forces attacked 36 of 44 provincial capitals and 5 of 6 major cities which was called the Tet Offensive. The worst fighting was in Hue, although there was highly publicized combat in Saigon.
A timeline of possibly connected events includes:
- Intensified battles for the northern provinces, far from major cities, with the People's Army of Viet Nam being willing to sustain exceptionally heavy casualties
- A general increase in small raids, without much military effect but a stronger psychological one that the Communist forces were everywhere and the Government of Vietnam could not provide security
- Major urban attacks in early 1968
The "Tet offensive" is usually restricted to the third; a major open question is whether the three classes of events were specifically related.
The mysterious context
It remains a mystery whether the Tet Offensive, and various actions leading up to it including the Battle of Con Thien and Battle of Khe Sanh, were a completele planned part of a strategy called Tet Mau Than or Tong Kong Kich/Tong Kong Ngia. (TCK/TCN, General Offensive/Uprising) [1] It is possible that it was, but that certain units started fighting prematurely and disrupted the schedule. It is unclear to which the Battle of Khe Sanh was part of an overall strategy to draw American forces away from the cities. Some agencies did not expect it, while others had suspected an oncoming offensive.
What is known or has been learned
- In 1967, there was a general increase in the number, although not necessarily the size, of Communist attacks.
- Also in 1967, there were several large and continued attacks, which might even be called sieges, of a type that had not previously been attempted. The PAVN seemed to accept very heavy casualties without an obvious reason.
- The large battles tended to be in isolated areas far from South Vietnamese prisoner interrogations.
- Interviews with defectors and prisoners, captured documents, and communications intelligence suggest that the North Vietnamese had some concept of a new strategy that would give them a clear victory, most likely in 1968 although earlier dates had been suggested.
- The commanding officer for operations in the South was dead, possibly due to combt wounds and possibly to natural causes, but who was sufficiently important that finding a successor could delay a planned offensive
- North Vietnamese doctrine, including material from public speeches and documents, appears to contain a concept of "popular uprising" (khnoi nghai), which is not in the Maoist protracted war theory that appeared to guide much of their doctrinal development.[2]
- A burst of major urban offensives, starting not at once, took place in late January and early February 1968. There are indications that these may have been expected to have much more decisive results.
Whether or not it was the fundamental North Vietnamese intention, the Tet Offensive proper had a major impact on U.S. public opinion, especially in an election year. However, the Tet Offensive had a devastating impact on Johnson's political position in the U.S., and in that sense was a strategic victory for the Communists. [3]
What is speculated
North Vietnamese planners expected popular uprising, but this almost completely failed to occur. Many South Vietnamese demonstrated stronger support for the ARVN. [4]
Some of the North Vietnamese attacks may have been launched prematurely.
Various acts on the South Vietnamese and U.S. side, some of which seem coincidental and others which were at least contingency plans, disrupted the attackers' plans to a striking effect. [5]
Defensive acts that were at least partially deliberate
- The attackers had planned to seize Radio Saigon and use it for major psychological warfare. While they did seize the main studio, the physically distant transmitter had prerecorded and noninflammatory material to be broadcast in the event of loss of studio content or if the studio material seemed questionable.
- Raiding forces included tank and artillery crews. When they attacked the South Vietnamese tank center, they found the tanks had been moved. The [[Army of the Republic of Viet Nam (ARVN) personnel had disabled to howitzers before they evacuated.
- LTG Fred Weyand, the commander of U.S. Forces in the III Corps tactical zone in the Saigon area, had been ordered to use most of his troops to sweep areas at the edge of the zone, but argued against moving them out of the inner defensive area. Ee was the American commander that had the greatest suspicion that a major attack was imminent, although not where it would strike. In such a situation, he wanted forces near the most valuable targets.
Defensive acts that were lucky
- General Cao Van Vien, chief of the ARVN Joint General Staff (JGS), had two remaining battalions, based in Saigon, in the strategic reserve. He had promised them to reinforce areas that had come under attack on January 30, but the flights to move them had not arrived at Saigon's Tan Son Nhut airfield. These were thus available for the critical defense of Saigon on January 31.[6]
- While the national operations center and the U.S. operations center for the Saigon area came under heavy artillery fire, there were no hits that disrupted command and control.
Intelligence and warning
In U.S. intelligence, three components appeared to have predicted the Tet action:[7]
- the Army communications intelligence group supporting MG Frederick C. Weyand's 3rd Corps[8]
- National Security Agency, although it did not recognize the scope of the offensive[9]
- Central Intelligence Agency Saigon Station; CIA headquarters disagreed with the field warnings
These failed, however, to make much impression outside the areas tactically concerned. Indeed, they were being delivered in a context where senior officials did not want to hear contradictory information; In September 1967, Assistant to the President for National Security Affairs Walt Rostow said that told the Agency that because President Lyndon Baines Johnson wanted some "useful intelligence on Vietnam for a change," the CIA should prepare a list of positive (only) developments in the war effort, which Director of Central Intelligence Richard Helms sent to Rostow with a dissenting cover note that Rostow removed. but Rostow pulled off that cover note and so was finally able to give the President a "good news" study from the CIA.[10]
Military intelligence
By December 9, MG Weyand asked GEN Westmoreland for permission to concentrate his troops around Saigon. ARVN troops, on 20 December, captured documents pointing to attack plans for Ban Me Thuot and Qui Nhon. [11]
NSA communications intelligence
Significant SIGINT came from several clusters of activity. One was from the "tri-border" area of Laos, Cambodia, and Vietnam, where the B-3 Front headquarters and 1st PAVN Division were known to be located. Another was in the Kontum-Pleiku area. East of the central highlands, 2nd PAVN Division was moving in the direction of coastal provinces including Quang Ngai, Phu Yen and Khanh Hoa. On the 21st, a forward headquarters was located 10 km from Hue. [12]
CIA Saigon station analysis
Reports from the Saigon station may have been strong warnings, but two assessments, from Bob Layton, on 21 November and 8 December 1967) based on human-source intelligence from prisoner interrogations and documents. They suggested that the PAVN was planning some type of decisive defeat for Allied forces in 1968. In conflict with the attention being given to Battle of Khe Sanh, these indicators pointed to urban terrorism coupled by military attacks on cities. There was a strong Communist belief that the GVN was so unpopular that an urban attack could irreparably damage confidence in the ARVN. These assessments also pointed to increasing international pressure on the Johnson administration to end the war.
A more detailed analysis, on December 8, described a distinct change in Communist thinking, away from the protracted war attritional model to something more decisive. It cited documentation of "an all-out military and political offensive during the 1967-68 winter-spring campaign [the period beginning around Tet] designed to gain decisive victory...large-scale continuous coordinated attacks by main force units, primarily in mountainous areas close to border sanctuaries"--a strategy subsequently reflected in the enemy's major attacks on Khe Sanh--and "widespread guerrilla attacks on large US/GVN units in rural and heavily populated areas." The PAVN saw the urban population as the center of gravity, not attrition to U.S. troops or the defeat of ARVN forces.
The plan was seen (emphasis added) "a serious effort to inflict unacceptable military and political losses on the Allies regardless of VC casualties during a US election year, in the hope that the US will be forced to yield to resulting domestic and international pressure and withdraw from South Vietnam." Even if the results did not force a settlement, the Communists would be in a "better position to continue a long-range struggle with a reduced force." He continued: "If the VC/NVN view the situation in this light, it is probably to their advantage to use their current apparatus to the fullest extent in hopes of fundamentally reversing current trends before attrition renders such an attempt impossible."
"In sum," the study's final sentence read, "the one conclusion that can be drawn from all of this is that the war is probably nearing a turning point and that the outcome of the 1967-68 winter-spring campaign will in all likelihood determine the future direction of the war."[13]
A 19 December report added more indicators that the NVA was preparing an all-out effort, although the Saigon analysts recognized the CIA Headquarters position that all of this exhortation might be an effort to bolster PAVN/VC morale. [14]
These field reports conflicted with a major Headquarters analysis of December 8, from the jointly by the Office of Current Intelligence, the Office of Economic Research, Office of National Estimates (O/NE), and Special Assistant to the DCI for Vietnam Affairs (SAVA). [15]
At the Central Intelligence Agency, Undersecretary of State Nicholas deB. Katzenbach and Assistant Secretary of State Philip Habib were being briefed about a suspected offensive, probably at the end of Tet, when the word of the first attacks came. [16]
Fighting in the Northern Provinces
=Con Thien
Khe Sanh
While the battle had been going on for some time, it intensified in Janury.
The fighting was most intense around Khe Sanh. There were three divisions of NVA regulars around Khe Sanh, possibly 25,000 men. Action began there around ten days before Tet, with probing attacks and exchanges of artillery fire. Two hill positions were captured on January 20, cutting the base from land routes. Attention in MACV and Washington was obsessed with Khe Sanh and other indicators of trouble were overlooked or down-graded.
The main assaults did not begin until February 5. Lang Vei was over-run on February 7 and the lines at Khe Sanh were very heavily attacked, the camp only being preserved by massive airstrikes and artillery barrages (over 30,000 sorties were flown in defence of the base). After this the tempo slowed, the battle became more of a siege, although there were further NVA assaults on the 17-18th and the 29th. Khe Sanh was officially relieved on April 6 and fighting ended around April 14. Possibly 8,000 NVA soldiers died around Khe Sanh.
Unusual raids
Urban Attacks
A number of sources believed the urban attacks started prematurely on January 29, Most of the urban attacks were on the night of January 30-31.
Urban areas outside Hue
Besides the symbolic targets in Saigon (III CTZ), and the very serious fighting in Hue (I CTZ, eight cities had substantial attacks.
Urban targets| City | ARVN CTZ | |
|---|---|---|
| Quang Nam | I CTZ | |
| Kontum | II CTZ | |
| My Tho | II CTZ | |
| Ban Met Thuot | II CTZ | |
| Nha Trang | II CTZ | |
| Ben Tre | ||
| Can Tho | ||
| Da Lat | II CTZ |
It was respect to Ben Tre that the comment was made, "it became necessary to destroy the town in order to save it."
Hue
The harshest fighting came in the old imperial capital of Hue. The city fell to the PAVN, which immediately set out to identify and execute thousands of government supporters among the civilian population. The allies fought back with all the firepower at their command. House to house fighting recaptured Hue on February 24. In Hue, five thousand enemy bodies were recovered, with 216 U.S. dead, and 384 ARVN fatalities. A number of civilians had been executed while the PAVN held the city.
Nationwide, the enemy lost tens of thousands killed, US lost 1,100 dead, ARVN 2,300. The people of South Vietnam did not rise up. Pacification, however, suspended in half the country, and a half million more people became refugees.
Saigon
They avoided American strongholds and targeted GVN government offices and ARVN installations, other than "media opportunities" such as attempting to a fight, by a 20-man suicide squad, of the U.S. Embassy. [17]
Real attacks, however, were directed at bases, especially major airbases in the Saigon area. Tan Son Nhut airbase, which was also the ARVN and MACV headquarters, was hit by around 700 men, with but 110 American casualties. Bien Hoa airbase was also attacked and twenty aircraft were destroyed.
Communist casualties in these two assaults and other actions in Saigon were over 1,100 men but they took control of large parts of the city for about a week. The longest fight was in the Chinese suburb of Cholon, where there was heavy damage and fighting for two weeks.
Other attacks on troops
Allied forces, especially U.S., actually were able to reconstitute quickly, but this reality did not gain press attention. A mortar attack on the Da Nang base destroyed a major supply warehouse, losing 16,000 line items of supply. The new logistics computer system was given a high priority code for Da Nang replacement; the computer sent replacement requests, for the 16,000 items now in zero supply, to U.S. suppy depots on the same day. Within 5 days, 78 percent of the requisitioned stock was in the supply-receiving line at Da Nang. [18]
References
- ↑ Hanyok, Robert J. (2002), Chapter 7 - A Springtime of Trumpets: SIGINT and the Tet Offensive, Spartans in Darkness: American SIGINT and the Indochina War, 1945-1975, Center for Cryptologic History, National Security Agency, p. 310
- ↑ Mao Tse-tung (1967), On Protracted War, Foreign Languages Press
- ↑ Willbanks, James H. (2006), The Tet Offensive: A Concise History
- ↑ Adams, Sam (1994), War of Numbers: An Intelligence Memoir, Steerforth Press
- ↑ Oberdorfer, p. 151
- ↑ Oberdorfer, pp. 149-150
- ↑ Ford, Harold R. (1997), Episode 3 1967-1968: CIA, the Order-of-Battle Controversy, and the Tet Offensive, CIA and the Vietnam Policymakers: Three Episodes 1962 - 1968, Center for the Study of Intelligence, Central Intelligence Agency, Ford Episode 3
- ↑ Ford Episode 3, General Weyand, to author, 17 April 1991. Weyand's communications intelligence battalion comander, LTC Norman Campbell, supports Weyand's accounts.
- ↑ Hanyok, pp. 326-333
- ↑ George Allen, The Indochina Wars, cited in Ford Episode 3
- ↑ Hanyok, p. 327
- ↑ Hanyok, p. 326
- ↑ Saigon telepouch FVSA 24242, 8 December 1967. CIA files, Job No. 80R01580R, DCI/ER Subject Files, Box 15, Folder 3, cited in Ford Episode 3
- ↑ Saigon telepouch SAIG 5624 (IN 69402), 19 December 1967. CIA files, Job No. 80B01721R, O/D/NFAC, Box 2, "Substantive Policy Files, DDI Vietnam Files, Folder 5. cited in Ford Episode 3
- ↑ CIA Memorandum, "A Review of the Situation in Vietnam," 8 December 1967, prepared jointly by the Office of Current Intelligence, the Office of Economic Research, O/NE, and SAVA. CIA files, Job No. 78T02095R, O/DDI, Box 1, Folder 1.cited in Ford Episode 3
- ↑ Oberdorfer, Don (2001), Tet! The Turning Point in the Vietnam War, JHU Press,pp. 18-20
- ↑ Oberdorfer, pp. 2-14
- ↑ Blank, Jonas L. (March-April 1973), "The Impact of Logistics Upon Strategy", Air University Review