Miltonia
| Miltonia | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
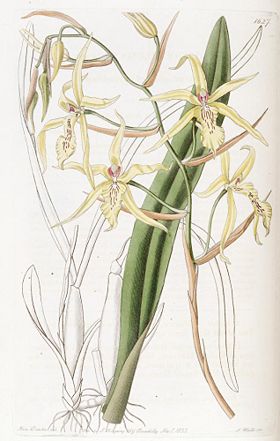
 Miltonia spectabilis
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Type species | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Miltonia spectabilis Lindl. 1837 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Species | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms | ||||||||||||||||||||
Miltonia is an orchid genus formed by nine epiphyte species and seven natural hybrids inhabitants of Brazilian Atlantic Forest, one species reaching the northeast of Argentina and east of Paraguay. This genus was established by John Lindley in 1837, when he described its type species, Miltonia spectabilis. Many species were attributed to Miltonia in the past, however, today, the species from Central America and from cooler areas on northwest of South America have been moved to other genera. Miltonia species have large and long lasting flowers, often in inflorescences with several of them. This fact, allied to being species that are easy to grow and to identify, make them a favorite of orchid collectors all over the world.
Despite today Miltonia is a well established genus, most of the species have been early classified under other genera as Cyrtochilum, Oncidium, Odondoglossum and Brassia. All species but M. kayasimae, discovered only in 1976, have been described between 1834 and 1850.
Distribution
Miltonia species range starts on the area of Missiones in the northeast of Argentina and east of Paraguay and spreads north along the Brazilian mountains of Serra do Mar and its branches up to the State of Pernambuco on Brazilian northeast. They occupy mostly areas between 200 and 1,500 meters of altitude meters, however the majority of the species are more often found about 600 to 900 meters. Miltonia species can be found from shady areas inside the forest to areas more exposed to the sun, however never are under full sunlight; usually in ventilated places where they receive plenty humidity during the night and early morning. They are always epiphyte and, because they grow very fast, each pseudobulb originating two new growths every year, they soon form large colonies.
Miltonia russelliana and M. flavescens are the ones with the widest dispersion and found at lower altitudes. M. flavescens is the only species that exists in countries other than Brazil and is also the one that spreads farther north. M russelliana range starts on Rio Grande do Sul and ends at Bahia State. M. regnellii is also widespread although does not go northern than Rio de Janeiro. M. moreliana is a species more common at lower altitudes and warmer areas existing from Rio to Pernambuco. Miltonia candida, M. clowesii and M. spectabilis are restricted to the four states of Region Southeast of Brazil. Miltonia cuneata is just from São Paulo and Rio and the one that grow at highest altitudes. M. kayasimae is the only species really rare; it has been found just a couple of times in a very restricted area close to Salesópolis, in São Paulo State.
Description
Miltonia are comparatively medium large orchid plants reaching about fifty centimeters height. They present subcaespitous growth, that means their pseudobulbs are not tightly packed but slightly spaced by a rhyzome, that is longer than on caespitous plants, with length between two and five centimeters. Their roots grow along the rhyzome in high numbers. They are white, comparatively thin, usually short and hardly branched. The rhyzome is covered by dried imbricating steaths which get increasingly larger at the base of pseudobulb becoming articulated foliar steaths that partially cover them. The pseudobulbs and leaves vary in color from yellowish bright light green to olive green depending on the species and to the amount of sunlight they are exposed to. They may be more oval and laterally highly flattened to slightly tetragonal and elongated and almost always bear two apical leaves. The leaves are narrow, flexible and hardly larger than three centimeters wide and forty long with the apexes rounded sometimes slightly pointed. Some species are about half of this size. The inflorescences are one or two per pseudobulb, shoot from their bases behind the protecting steaths. They are erect and never branched, often longer than the leaves, bearing from one to twelve moderately spaced flowers that open at the same time or in succession holding three or four opened all the time, when the older fades a new one opens. The older flowers of species with white lips that open in succession usually get yellower about the time the next flower opens although they still last one more week before fading. The first to bloom is M. cuneata, during late winter, but the majority of species bloom from late spring to late summer.
The flowers of Miltonia vary from four to fifteen centimeters across; the larger are the ones with fewer flowers. Their colors vary from entirely white and pink to dark purple, pale yellow or lilac when plain, or they may highly spotted but then usually they are greenish or brownish with a contrasting labellum often white with purple dots, stains or veins close to the base. The petals and sepals shapes are highly variable from species to species but always somewhat similar to each other within a species. They may be erect and flat or sometimes less open. The labellum is simple or very slightly lobed, usually very wide and showy without salient calli although normally showing more or less subtle keeled thickenings close to the base, usually of different colors; it is much larger and wider than the other segmentes, often flat but in M. candida"' embraces the column and in all species it is slighly fused to the column at their bases. The short column does not have a foot and presents two lateral auricules sometimes merged to each other through a fringe that surrounds the superior edge of the clinandrium. The anther is apical and bears two yellow hard pollinia. They possibly are pollinated by bees.
Taxonomic notes
The first species to be described, among the ones today classified under the genus Miltonia, was originally published by John Lindley, in 1834, as Cyrtochilum flavescens. In this description Lindley notices that the flowers of this species turn orange color when drying and, for some confusion regarding the origin of the species, attributes it to Mexico instead of Brazil.
Three years later Lindley received from Mr. Loddiges and from George Baker two other specimens of a very distinctive new species. Recognizing then this should in fact be a new genus, he proposed the name Miltonia to it as a homage to Lord Fitzwilliam Milton, an English orchid enthusiast. Lindley states then that the limits between a number of Oncidiinae genera, Cyrtochilum, Oncidium, Odondoglossum, Brassia and Miltonia, at that time classified as Vandaea, were yet to be perfectly established; although closely related, the differences should possibly be: Oncidium has a column with two ears and labellum distinctively lobed; Miltonia has a column with two ears and an entire labellum partially united to the column base; Odontoglossum and Cyrtochilum have winged columns and entire labelli but the former has it partially united to the column; and Brassia does not have any appendages on the column.
Species
The rhyzome is longer on the species of M. spectabilis group.