Pythagorean theorem
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
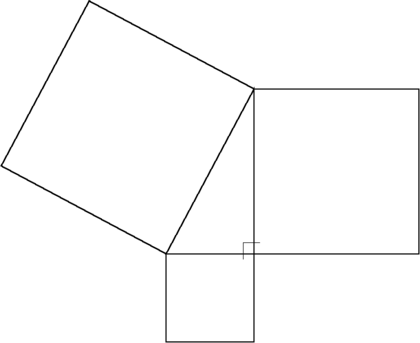
The Pythagorean theorem: The sum of the areas of the two squares on the legs (the sides that meet at a right angle) equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle).
In Euclidean geometry, the Pythagorean theorem states that:
- The sum of the areas of the squares on the legs of a right triangle equals the area of the square on the hypotenuse.
The "legs" are the two sides of the triangle that meet at a right angle. The hypotenuse is the other side—the side opposite the right angle.