Law of cosines
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
The law of cosines is a useful identity for determining an angle or the length of one side of a triangle, when given two angles and three lenghts or three angles and two lengths, respectively. When dealing with a right triangle, the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean theorem because the cos(90) is zero. To determine the areas of triangles, see the Law of sines.
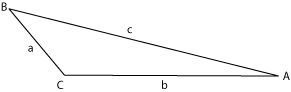
where a, b and c are the sides of the triangle opposite to angles A, B and C, respectively (see image).